mac安装unsloth
mac 安装unsloth 遇到的那些坑
目录
- mac 安装unsloth 遇到的那些坑
- 1. unsloth官方主分支是不支持mac,只能使用推荐的非官方版本
- 2. unsloth的Mac版:shashikanth-a:apple_silicon_support
- 3. 使用这一版本的unsloth
- 3.1 通过命令行查看帮助
- 3.2 简单的使用示例
1. unsloth官方主分支是不支持mac,只能使用推荐的非官方版本
登陆unsloth的github主页可以看到安装只支持windows和linux,不支持macOS。
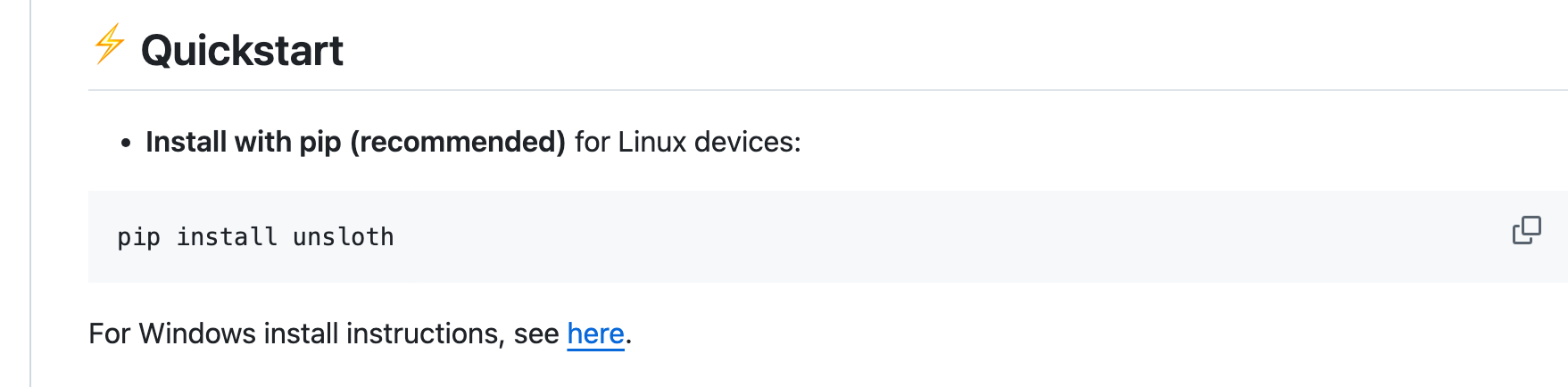
进入issue搜索mac,可以发现,在2023年就有人提出了增加mac支持的建议,这几个issue比如4至今还是开放着的。
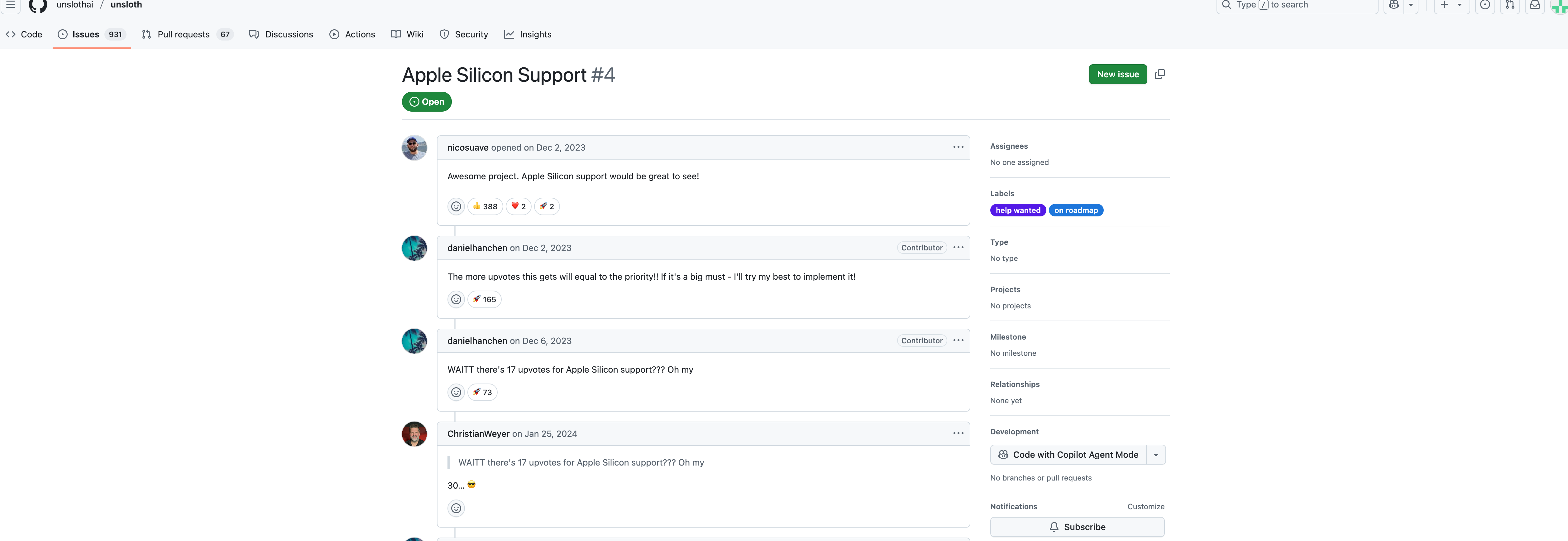
翻到底下,可以看到2025年3月,unsloth项目的collaborator接到了一个合并请求#1289,这个请求实现了unsloth在mac上部署。但是还需要验证,所以需要大家安装测试其性能,才能决定是否合并到unsloth的主分支上。
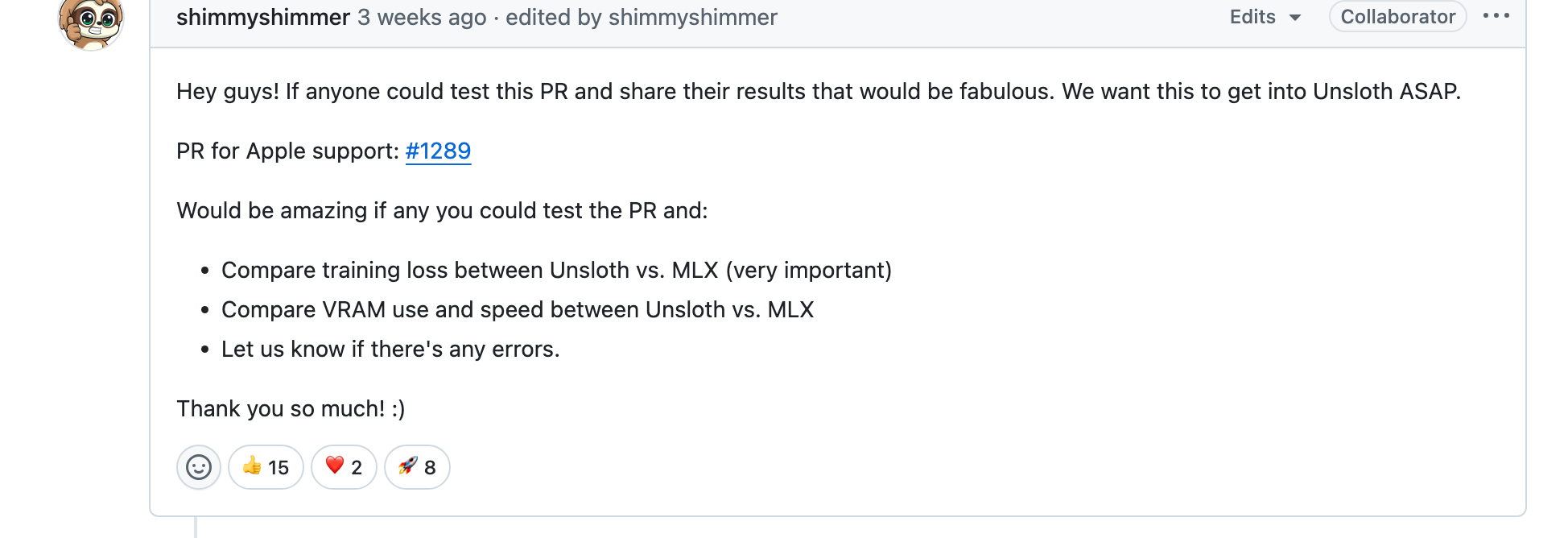
我们可以打开#1289合并请求,看看作者怎么做的。
2. unsloth的Mac版:shashikanth-a:apple_silicon_support
打开unsloth的PR#1289,可以看到shashikanth-a制作了一个苹果芯片支持的版本 ,并发布在了他自己的fork上,并请求合并进unsloth的main分支。main分支肯定是不给合并的,如果以后测试结果不错应该会创建相应的apple分支。
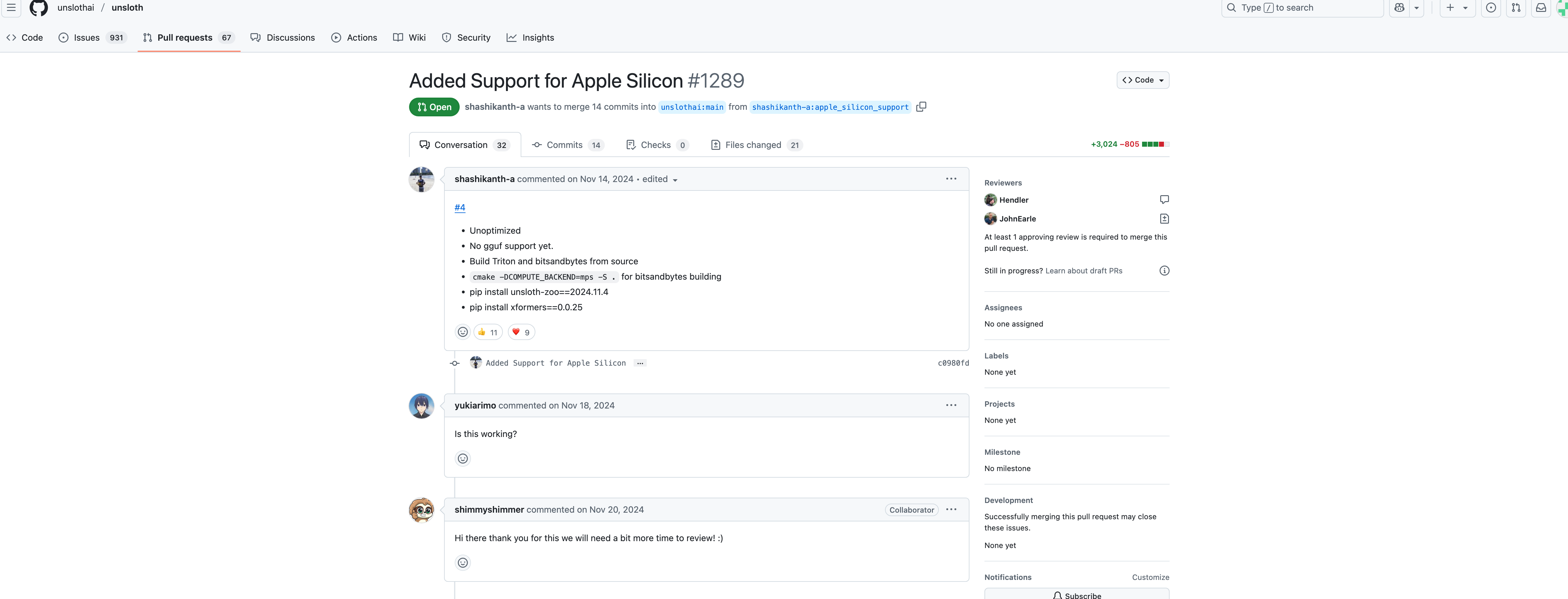
我们进入这个支持苹果芯片的版本看看
该版本的链接为:https://github.com/shashikanth-a/unsloth/tree/apple_silicon_support
请注意不要使用其主分支main,使用apple_silicon_support分支
对了,当前unsloth支持的python版本从3.9-3.12,最新默认安装的3.13不支持,创建环境记得强制要求python=3.12,如果忘记了记得使用conda install python=3.12 进行强制降级。
下载命令如下:
git clone https://github.com/shashikanth-a/unsloth.git -b apple_silicon_support. #这是下载代码,我试了不好使,可以直接下载zip
cd unsloth # 进入到这个项目文件夹内,在文件夹内应该存在pyproject.toml文件
python -m venv myvenvname #在当前位置创建一个虚拟环境,建议使用conda提前创建好,另外,强烈建议新建一个环境,这个版本安装了乱七八糟很多东西
source venv/bin/activate # 激活环境
pip install -e ".[huggingface]" # 根据pyproject.toml文件进行安装
肉眼可见的安装了这一大堆东西
3. 使用这一版本的unsloth
3.1 通过命令行查看帮助
感谢作者
python unsloth-cli.py --help
会通过命令行蹦出使用指导,还是很全面的
🦥 Unsloth: Will patch your computer to enable 2x faster free finetuning.
usage: unsloth-cli.py [-h] [--model_name MODEL_NAME] [--max_seq_length MAX_SEQ_LENGTH]
[--dtype DTYPE] [--load_in_4bit] [--dataset DATASET] [--r R]
[--lora_alpha LORA_ALPHA] [--lora_dropout LORA_DROPOUT] [--bias BIAS]
[--use_gradient_checkpointing USE_GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING]
[--random_state RANDOM_STATE] [--use_rslora]
[--loftq_config LOFTQ_CONFIG]
[--per_device_train_batch_size PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE]
[--gradient_accumulation_steps GRADIENT_ACCUMULATION_STEPS]
[--warmup_steps WARMUP_STEPS] [--max_steps MAX_STEPS]
[--learning_rate LEARNING_RATE] [--optim OPTIM]
[--weight_decay WEIGHT_DECAY] [--lr_scheduler_type LR_SCHEDULER_TYPE]
[--seed SEED]
[--report_to {azure_ml,clearml,codecarbon,comet_ml,dagshub,dvclive,flyte,mlflow,neptune,tensorboard,wandb,all,none}]
[--logging_steps LOGGING_STEPS] [--adapter_file ADAPTER_FILE]
[--output_dir OUTPUT_DIR] [--save_model]
[--save_method {merged_16bit,merged_4bit,lora}] [--save_gguf]
[--save_path SAVE_PATH]
[--quantization QUANTIZATION [QUANTIZATION ...]] [--push_model]
[--push_gguf] [--hub_path HUB_PATH] [--hub_token HUB_TOKEN]
🦥 Fine-tune your llm faster using unsloth!
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
🤖 Model Options:
--model_name MODEL_NAME
Model name to load
--max_seq_length MAX_SEQ_LENGTH
Maximum sequence length, default is 2048. We auto support RoPE
Scaling internally!
--dtype DTYPE Data type for model (None for auto detection)
--load_in_4bit Use 4bit quantization to reduce memory usage
--dataset DATASET Huggingface dataset to use for training
🧠 LoRA Options:
These options are used to configure the LoRA model.
--r R Rank for Lora model, default is 16. (common values: 8, 16, 32, 64,
128)
--lora_alpha LORA_ALPHA
LoRA alpha parameter, default is 16. (common values: 8, 16, 32, 64,
128)
--lora_dropout LORA_DROPOUT
LoRA dropout rate, default is 0.0 which is optimized.
--bias BIAS Bias setting for LoRA
--use_gradient_checkpointing USE_GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING
Use gradient checkpointing
--random_state RANDOM_STATE
Random state for reproducibility, default is 3407.
--use_rslora Use rank stabilized LoRA
--loftq_config LOFTQ_CONFIG
Configuration for LoftQ
🎓 Training Options:
--per_device_train_batch_size PER_DEVICE_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE
Batch size per device during training, default is 2.
--gradient_accumulation_steps GRADIENT_ACCUMULATION_STEPS
Number of gradient accumulation steps, default is 4.
--warmup_steps WARMUP_STEPS
Number of warmup steps, default is 5.
--max_steps MAX_STEPS
Maximum number of training steps.
--learning_rate LEARNING_RATE
Learning rate, default is 2e-4.
--optim OPTIM Optimizer type.
--weight_decay WEIGHT_DECAY
Weight decay, default is 0.01.
--lr_scheduler_type LR_SCHEDULER_TYPE
Learning rate scheduler type, default is 'linear'.
--seed SEED Seed for reproducibility, default is 3407.
📊 Report Options:
--report_to {azure_ml,clearml,codecarbon,comet_ml,dagshub,dvclive,flyte,mlflow,neptune,tensorboard,wandb,all,none}
The list of integrations to report the results and logs to. Supported
platforms are: 'azure_ml', 'clearml', 'codecarbon', 'comet_ml',
'dagshub', 'dvclive', 'flyte', 'mlflow', 'neptune', 'tensorboard',
and 'wandb'. Use 'all' to report to all integrations installed,
'none' for no integrations.
--logging_steps LOGGING_STEPS
Logging steps, default is 1
💾 Save Model Options:
--adapter_file ADAPTER_FILE
Adapters file name
--output_dir OUTPUT_DIR
Output directory
--save_model Save the model after training
--save_method {merged_16bit,merged_4bit,lora}
Save method for the model, default is 'merged_16bit'
--save_gguf Convert the model to GGUF after training
--save_path SAVE_PATH
Path to save the model
--quantization QUANTIZATION [QUANTIZATION ...]
Quantization method for saving the model. common values ('f16',
'q4_k_m', 'q8_0'), Check our wiki for all quantization methods
https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth/wiki#saving-to-gguf
🚀 Push Model Options:
--push_model Push the model to Hugging Face hub after training
--push_gguf Push the model as GGUF to Hugging Face hub after training
--hub_path HUB_PATH Path on Hugging Face hub to push the model
--hub_token HUB_TOKEN
Token for pushing the model to Hugging Face hub
3.2 简单的使用示例
可以参照这个示例,更多理解如何使用mac版的非官方unsloth
from unsloth.mlx import mlx_utils
from unsloth.mlx import lora as mlx_lora
from unsloth import is_bfloat16_supported
from transformers.utils import strtobool
from datasets import Dataset
import logging
import os
import argparse
# Create args object with the same parameters as the CLI script
args = argparse.Namespace(
# Model options
model_name="unsloth/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct", # Or whatever model you're using
max_seq_length=2048,
dtype="bfloat16" if is_bfloat16_supported() else "float16",
load_in_4bit=True,
# LoRA options
r=16,
lora_alpha=16,
lora_dropout=0.1,
bias="none",
use_gradient_checkpointing="unsloth",
random_state=3407,
use_rslora=False,
loftq_config=None,
# Training options
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
warmup_steps=5,
max_steps=100, # Smaller for quick testing
learning_rate=2e-4,
optim="adamw_8bit",
weight_decay=0.01,
lr_scheduler_type="linear",
seed=3407,
# Reporting options
output_dir="outputs",
report_to="tensorboard",
logging_steps=1,
# Save options
adapter_file="adapters.safetensors",
save_model=True,
save_method="merged_16bit",
save_gguf=False,
save_path="model",
quantization="q8_0"
)
logging.getLogger('hf-to-gguf').setLevel(logging.WARNING)
print("Loading pretrained model. This may take a while...")
model, tokenizer, config = mlx_utils.load_pretrained(
args.model_name,
dtype=args.dtype,
load_in_4bit=args.load_in_4bit
)
print("Model loaded")
# Configure PEFT model
alpaca_prompt = """Below is an instruction that describes a task, paired with an input that provides further context. Write a response that appropriately completes the request.
### Instruction:
{}
### Input:
{}
### Response:
{}"""
EOS_TOKEN = tokenizer.eos_token # Must add EOS_TOKEN
def formatting_prompts_func(examples):
instructions = examples["instruction"]
inputs = examples["input"]
outputs = examples["output"]
texts = []
for instruction, input, output in zip(instructions, inputs, outputs):
text = alpaca_prompt.format(instruction, input, output) + EOS_TOKEN
texts.append(text)
return {"text": texts}
use_modelscope = strtobool(os.environ.get('UNSLOTH_USE_MODELSCOPE', 'False'))
# Create a super basic test dataset with just a few examples
basic_data = {
"instruction": [
"Summarize the following text",
"Translate this to French",
"Explain this concept",
"Write a poem about",
"List five advantages of",
"Provide examples of"
],
"input": [
"The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.",
"Hello world",
"Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence",
"autumn leaves falling",
"renewable energy",
"good leadership qualities"
],
"output": [
"A fox quickly jumps over a dog.",
"Bonjour le monde",
"Machine learning is an AI approach where systems learn patterns from data",
"Golden leaves drift down
Dancing in the autumn breeze
Nature's last hurrah",
"Renewable energy is sustainable, reduces pollution, creates jobs, promotes energy independence, and has lower operating costs.",
"Good leaders demonstrate empathy, clear communication, decisiveness, integrity, and the ability to inspire others."
]
}
# Convert to HuggingFace Dataset format
dataset = Dataset.from_dict(basic_data)
print("Dataset initialized")
# Use the same formatting function as before
dataset = dataset.map(formatting_prompts_func, batched=True)
print("Data is formatted and ready!")
# Split into train/test with appropriate size for small dataset
datasets = dataset.train_test_split(test_size=0.33)
print(f"Training examples: {len(datasets['train'])}, Test examples: {len(datasets['test'])}")
# Train model
print("Starting training")
mlx_lora.train_model(args, model, tokenizer, datasets["train"], datasets["test"])
示例运行结果
Trainable parameters: 0.143% (4.588M/3212.750M)
Starting training..., iters: 100
Iter 1: Val loss 2.323, Val took 1.660s
Iter 1: Train loss 2.401, Learning Rate 0.000e+00, It/sec 0.580, Tokens/sec 117.208, Trained Tokens 202, Peak mem 2.661 GB
mx.metal.get_peak_memory is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use mx.get_peak_memory instead.
Iter 2: Train loss 2.134, Learning Rate 0.000e+00, It/sec 0.493, Tokens/sec 119.230, Trained Tokens 444, Peak mem 2.810 GB
Iter 3: Train loss 2.401, Learning Rate 0.000e+00, It/sec 0.539, Tokens/sec 108.948, Trained Tokens 646, Peak mem 2.810 GB
Iter 4: Train loss 2.134, Learning Rate 0.000e+00, It/sec 0.438, Tokens/sec 105.966, Trained Tokens 888, Peak mem 2.810 GB
Iter 5: Train loss 2.401, Learning Rate 0.000e+00, It/sec 0.566, Tokens/sec 114.282, Trained Tokens 1090, Peak mem 2.810 GB