基于muduo库实现高并发服务器
文章目录
- 一、项目介绍
- 二、HTTP服务器
- 1.概念
- 2.Reactor模型
- 2.1单Reactor单线程:单I/O多路复用+业务处理
- 2.2单Reactor多线程:单I/O多路复用+线程池(业务处理)
- 2.3多Reactor多线程:多I/O多路复用+线程池(业务处理)
- 三、前置知识技术点功能用例
- 1.C++11中的bind
- 2.简单的秒级定时任务实现
- 3.正则库的简单使用
- 4.通用类型any类型的实现
- 四、功能模块划分
- 1.SERVER模块
- 1.1Buffer模块
- 1.2.Socket模块
- 1.3Channel模块
- 1.4Connection模块
- 1.5Acceptor模块
- 1.6TimerQueue模块
- 1.7Poller模块
- 1.8EventLoop模块
- 1.9TcpServer模块
- 2.HTTP协议模块
- 2.1Util模块
- 2.2HttpRequest模块
- 2.3HttpResponse模块
- 2.4HttpContext模块
- 2.5HttpServer模块
- 五、模块关系图
- 六、SERVER服务器模块实现
- 1.缓冲区Buffer类实现
- 2.日志宏的实现
- 3.Socket模块实现
- 4.Channel模块实现
- 3.描述符事件监控Poller类实现
- 4.EventLoop类的实现
- 4.通信连接管理Connection类实现
- 5.监听描述符管理Acceptor类实现
- 6.LoopThread类的实现
- 8.LoopThreadPool类的实现
- 9.服务器TcpServer类实现
- 10.基于TcpServer实现回显服务器
- 七、HTTP协议模块
- 1.Util工具类实现
- 2.HttpRequest请求类实现
- 3.HttpResponse响应类实现
- 4.HttpContext上下文类实现
- 5.HttpServer类实现
- 6.HttpServer 简单测试
- 八、性能测试
- 1. 服务器长连接测试
- 2. 服务器超时连接测试
- 3.服务器错误请求测试
- 4.服务器业务处理超时测试
- 5.服务器同时多条请求测试
- 服务器大文件传输测试
- 服务器性能压力测试
- 4.服务器业务处理超时测试
- 5.服务器同时多条请求测试
- 服务器大文件传输测试
- 服务器性能压力测试
一、项目介绍
本项目主要是模仿 muduo 库实现一个以主从 Reactor 为模型,以 OneThreadOneEventLoop 为事件驱动的高并发服务器组件。通过这个服务器组件,我们可以简洁快速的搭建出一个高性能的 TCP 服务器。并且组件内部会提供不同的应用层协议支持,组件使用者可以通过这些协议快速的完成一个应用服务器的搭建。
muduo 源码 – https://github.com/chenshuo/muduo/tree/master/muduo
muduo 介绍 – https://www.cyhone.com/articles/analysis-of-muduo/
二、HTTP服务器
1.概念
HTTP(Hyper Text Transfer Protocol),超文本传输协议是应用层协议,是一种简单的请求-响应协议(客户端根据自己的需要向服务器发送请求,服务器针对请求提供服务,完毕后通信结束)。但是需要注意的是HTTP协议是一个运行在TCP协议之上的应用层协议,这一点本质上是告诉我们,HTTP服务器其实就是个TCP服务器,只不过在应用层基于HTTP协议格式进行数据的组织和解析来明确客户端的请求并完成业务处理。
因此实现HTTP服务器简单理解,只需要以下几步即可
1.搭建一个TCP服务器,接收客户端请求。
2.以HTTP协议格式进行解析请求数据,明确客户端目的。
3.明确客户端请求目的后提供对应服务。
4.将服务结果⼀HTTP协议格式进行组织,发送给客户端
实现一个HTTP服务器很简单,但是实现一个高性能的服务器并不简单,这个单元中将讲解基于Reactor模式的高性能服务器实现。当然准确来说,因为我们要实现的服务器本身并不存在业务,咱们要实现的应该算是一个高性能服务器基础库,是一个基础组件。
2.Reactor模型
Reactor 模式,是指通过一个或多个输入同时传递给服务器进行请求处理时的事件驱动处理模式。服务端程序处理传入多路请求,并将它们同步分派给请求对应的处理线程,Reactor 模式也叫Dispatcher 模式。简单理解就是使用 I/O多路复用统一监听事件,收到事件后分发给处理进程或线程,是编写高性能网络服务器的必备技术之一。
2.1单Reactor单线程:单I/O多路复用+业务处理

单Reactor单线程:在单个线程中进行事件监控并处理
服务端处理思想:事件驱动触发模式
谁发送了数据,谁触发了事件就处理谁
技术支撑点:I/O多路转接技术
1.通过IO多路复用模型对所有的客户端进行IO事件监控
2.触发事件后,进行事件处理。哪个客户端触发了事件,就去处理谁:接收它的请求,进行业务处理,进行响应
a. 如果是新建连接请求,则获取新建连接,并添加至多路复用模型进行事件监控。
b. 如果是数据通信请求,则进行对应数据处理(接收数据,处理数据,发送响应)。
优点:所有操作均在同一线程中完成,思想流程较为简单,不涉及进程/线程间通信及资源争抢问题。因为是单线程操作,操作都是串行化的,思想较为简单,编码流程也较为简单〈不用考虑进程或者线程间的通信,以及安全问题)
缺点:因为所有的事件监控以及业务处理都是在一个线程中完成的,无法有效利用CPU多核资源,因此很容易造成性能瓶颈
适用场景:适用于客户端数量较少,且处理速度较为快速的场景。(处理较慢或活跃连接较多,会导致串行处理的情况下,后处理的连接长时间无法得到响应)
2.2单Reactor多线程:单I/O多路复用+线程池(业务处理)
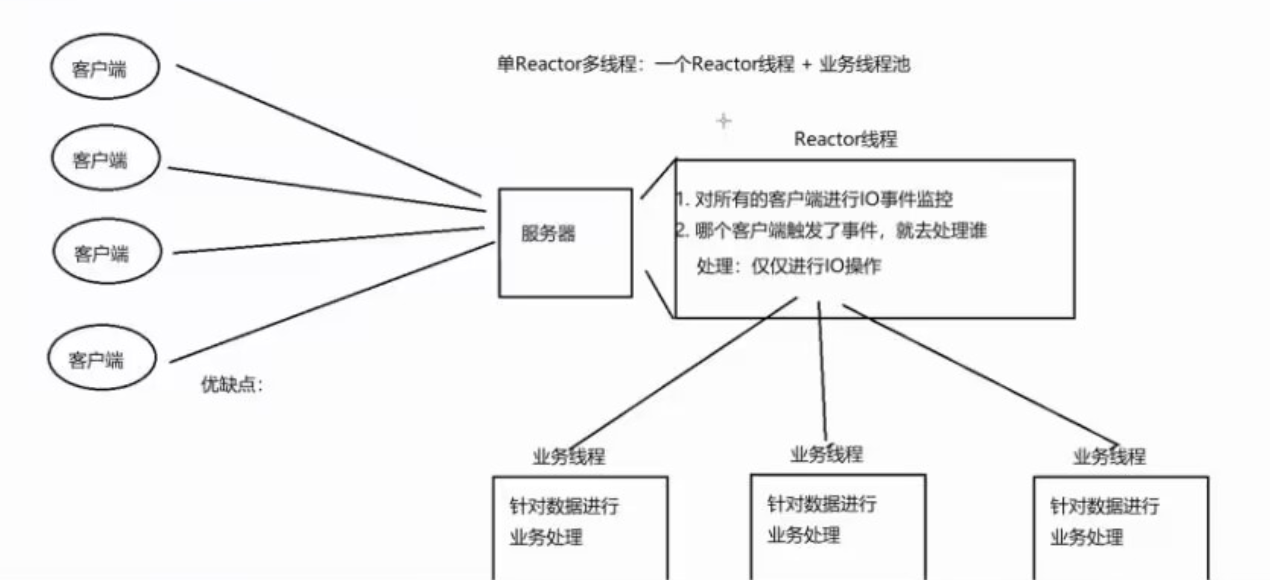
1.Reactor线程通过I/O多路复用模型进行客户端请求监控
2.触发事件后,进行事件处理
对所有的客户端进行IO事件监控,哪个客户端触发了事件,就去处理谁 处理:仅仅进行IO操作
a. 如果是新建连接请求,则获取新建连接,并添加至多路复用模型进行事件监控。
b. 如果是数据通信请求,则接收数据后分发给Worker线程池进行业务处理。
c. 工作线程处理完毕后,将响应交给Reactor线程进行数据响应
优点:充分利用了CPU多核资源,处理效率可以更高,降低了代码的耦合度
缺点:多线程间的数据共享访问控制较为复杂,单个Reactor 承担所有事件的监听和响应,在单线程中运行,高并发场景下容易成为性能瓶颈。在单个Reactor线程中,包含了对所有客户端的事件监控,以及所有客户端的IO操作,不利于高并发场景(每一个时刻都有很多客户端连接),来不及进行新的客户端连接处理
2.3多Reactor多线程:多I/O多路复用+线程池(业务处理)

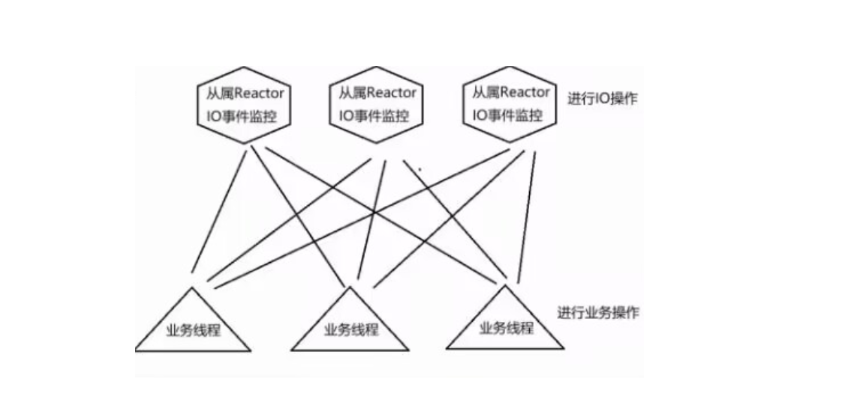
1.在主Reactor中处理新连接请求事件,有新连接到来则分发到子Reactor中监控
2.在子Reactor中进行客户端通信监控,有事件触发,则接收数据分发给Worker线程池
4.Worker线程池分配独立的线程进行具体的业务处理
a. 工作线程处理完毕后,将响应交给子Reactor线程进行数据响应
多Reactor多线程模式:基于单reactor多线程的缺点考虑,如果IO的时候,有连接到来无法处理,因此将连接处理单独拎出来。因此让一个Reactor线程仅仅进行新连接的处理,让其他的Reactor线程进行IO处理,IO Reactor线程拿到数据分发给业务线程池进行业务处理。因此多Reactor多线程模式,也叫做主从Reactor模型。
主Reactor线程:进行新连接事件监控。
**从属Reactor线程:进行lO事件监控 **
业务线程池:进行业务处理
优点:充分利用了CPU多核资源,并且可以进行合理分配,主从Reactor各司其职
但是大家也要理解:执行流并不是越多越好,因为执行流多了,反而会增加CPU切换调度的成本
目标定位:One Thread One Loop主从Reactor模型高并发服务器
咱们要实现的是主从Reactor模型服务器,也就是主Reactor线程仅仅监控监听描述符,获取新建连接,保证获取新连接的高效性,提高服务器的并发性能。主Reactor获取到新连接后分发给子Reactor进行通信事件监控。而子Reactor线程监控各自的描述符的读写事件进行数据读写以及业务处理。即子Reactor完成IO事件监控,IO操作,以及业务处理。One Thread One Loop的思想就是把所有的操作都放到一个线程中进行,一个线程对应一个事件处理的循环。当前实现中,因为并不确定组件使用者的使用意向,因此并不提供业务层工作线程池的实现,只实现主从Reactor,而Worker工作线程池,可由组件库的使用者的需要自行决定是否使用和实现
三、前置知识技术点功能用例
1.C++11中的bind
bind (Fn&& fn, Args&&... args);
官方文档对于bind接口的概述解释:Bind function arguments
我们可以将bind接口看作是一个通用的函数适配器,它接受一个函数对象,以及函数的各项参数,然后返回一个新的函数对象,但是这个函数对象的参数已经被绑定为设置的参数。运行的时候相当于总是调用传入固定参数的原函数。
但是如果进行绑定的时候,给与的参数为 std::placeholders::_1, _2... 则相当于为新适配生成的函数对象的调用预留一个参数进行传递。
基于bind的作用,当我们在设计一些线程池,或者任务池的时候,就可以将将任务池中的任务设置为函数类型,函数的参数由添加任务者直接使用bind进行适配绑定设置,而任务池中的任务被处理,只需要取出一个个的函数进行执行即可。
这样做有个好处就是,这种任务池在设计的时候,不用考虑都有哪些任务处理方式了,处理函数该如何设计,有多少个什么样的参数,这些都不用考虑了,降低了代码之间的耦合度。
#include 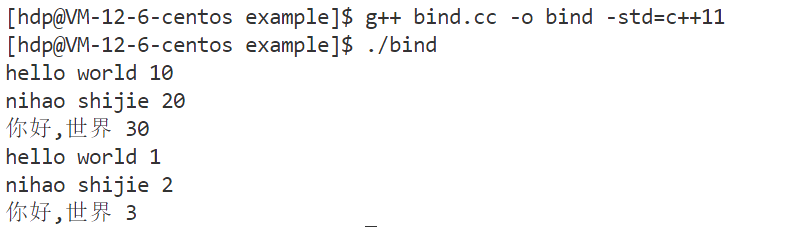
2.简单的秒级定时任务实现
在当前的高并发服务器中,我们不得不考虑一个问题,那就是连接的超时关闭问题。我们需要避免一个连接长时间不通信,但是也不关闭,空耗资源的情况。这时候我们就需要一个定时任务,定时的将超时过期的连接进行释放。
Linux提供给我们的定时器:
#include 使用案例:
#include 上边例子,是一个定时器的使用示例,是每隔3s钟触发一次定时器超时,否则就会阻塞在read读取数据这里。
基于这个例子,则我们可以实现每隔3s,检测一下哪些连接超时了,然后将超时的连接释放掉。
时间轮思想:
上述的例子,存在一个很大的问题,每次超时都要将所有的连接遍历一遍,如果有上万个连接,效率无疑是较为低下的。这时候大家就会想到,我们可以针对所有的连接,根据每个连接最近一次通信的系统时间建立一个小根堆,这样只需要每次针对堆顶部分的连接逐个释放,直到没有超时的连接为止,这样也可以大大提高处理的效率。
上述方法可以实现定时任务,但是这里给大家介绍另一种方案:时间轮
时间轮的思想来源于钟表,如果我们定了一个3点钟的闹铃,则当时针走到3的时候,就代表时间到了。
同样的道理,如果我们定义了一个数组,并且有一个指针,指向数组起始位置,这个指针每秒钟向后走动一步,走到哪里,则代表哪里的任务该被执行了,那么如果我们想要定一个3s后的任务,则只需要将任务添加到tick+3的位置,则每秒钟走一步,三秒钟后tick走到对应位置,这时候执行对应位置的任务即可。
但是,同一时间可能会有大批量的定时任务,因此我们可以给数组对应位置下拉一个数组,这样就可以在同一个时刻上添加多个定时任务了。
当然,上述操作也有一些缺陷,比如我们如果要定义一个60s后的任务,则需要将数组的元素个数设置为60才可以,如果设置一小时后的定时任务,则需要定义3600个元素的数组,这样无疑是比较麻烦的。
因此,可以采用多层级的时间轮,有秒针轮,分针轮,时针轮, 60 但是,我们也得考虑一个问题,当前的设计是时间到了,则主动去执行定时任务,释放连接,那能不能在时间到了后,自动执行定时任务呢,这时候我们就想到一个操作–类的析构函数。 一个类的析构函数,在对象被释放时会自动被执行,那么我们如果将一个定时任务作为一个类的析构函数内的操作,则这个定时任务在对象被释放的时候就会执行。 但是仅仅为了这个目的,而设计一个额外的任务类,好像有些不划算,但是,这里我们又要考虑另一个问题,那就是假如有一个连接建立成功了,我们给这个连接设置了一个30s后的定时销毁任务,但是在第10s的时候,这个连接进行了一次通信,那么我们应该是在第30s的时候关闭,还是第40s的时候关闭呢?无疑应该是第40s的时候。也就是说,这时候,我们需要让这个第30s的任务失效,但是我们该如何实现这个操作呢? 这里,我们就用到了智能指针shared_ptr,shared_ptr有个计数器,当计数为0的时候,才会真正释放一个对象,那么如果连接在第10s进行了一次通信,则我们继续向定时任务中,添加一个30s后(也就是第40s)的任务类对象的shared_ptr,则这时候两个任务shared_ptr计数为2,则第30s的定时任务被释放的时候,计数-1,变为1,并不为0,则并不会执行实际的析构函数,那么就相当于这个第30s的任务失效了,只有在第40s的时候,这个任务才会被真正释放。 上述过程就是时间轮定时任务的思想了,当然这里为了更加简便的实现,进行了一些小小的调整实现。 总结: 1.同一时刻的定时任务只能添加一个,需要考虑如何在同一时刻支持添加多个定时任务 解决方案: 将时间轮的一维数组设计为二维数组(时间轮一位数组的每一个节点也是一个数组) 2.假设当前的定时任务是一个连接的非活跃销毁任务,这个任务什么时候添加到时间轮中比较合适 一个连接30s内都没有通信,则是一个非活跃连接,这时候就销毁。但是一个连接如果在建立的时候添加了一个30s后销毁的任务,但是这个连接30s内人家有数据通信,在第30s的时候不是一个非活跃连接。 思想:需要在一个连接有IO事件产生的时候,延迟定时任务的执行 作为一个时间轮定时器,本身并不关注任务类型,只要是时间到了就需要被执行。 解决方案:类的析构函数+智能指针shared_ptr,通过这两个技术可以实现定时任务的延时 1.使用一个类,对定时任务进行封装,类实例化的每一个对象,就是一个定时任务对象,当对象被销毁的时候,再去执行定时任务(将定时任务的执行,放到析构函数中) 2.shared ptr用于对new的对象进行空间管理,当shared_ptr对一个对象进行管理的时候,内部有一个计数器,计数器为0的时候,则释放所管理的对象 当pi和pi1中任意一个被释放的时候,只是计数器-1,因此他们管理的a对象并没有被释放,只有当pi和pi1都被释放了,计数器为0了,这时候才会释放管理的a对象 基于这个思想,我们可以使用shared_ptr来管理定时器任务对象 但是std::shared_ptr pi2(a);但是如果pi2是针对的原始对象构造的。并不会跟pi和pi1,共享计数 使用案例: 正则表达式(regular expression)描述了一种字符串匹配的模式(pattern),可以用来检查一个串是否含有某种子串、将匹配的子串替换或者从某个串中取出符合某个条件的子串等。 正则表达式的使用,可以使得HTTP请求的解析更加简单(这里指的时程序员的工作变得的简单,这并不代表处理效率会变高,实际上效率上是低于直接的字符串处理的),使我们实现的HTTP组件库使用起来更加灵活。 我们可以在这里学习相关的语法:正则表达式教程–菜鸟教程 正则表达式的简单案例: HTTP请求行的匹配 在本项目中,我们要实现一个高并发的服务器组件,能够的接收并处理客户端发送过来的请求,就必然涉及到与客户端的通信,而通信就必然涉及到对套接字的操作;同时,由于 TCP 是面向字节流的,因此服务器在接收客户端数据的时候就可能出现 socket 中的数据不足一条完整请求的情况,此时我们请求处理到一半时就需要停下来等待 socket 中下一次的数据到来。 因此我们需要为客户端连接设置一个请求处理的上下文,用来保存请求接收、解析以及处理的状态,它决定着对于下一次从缓冲区中取出的数据如何进行处理、从哪里开始处理等。同时,对于一条完整的请求,我们还需要对其进行解析,得到各种关键的要素,比如 HTTP 请求中的请求方法、请求URL、HTTP版本等,这些信息都会被保存在请求处理上下文中。 那么我们应该如何保存请求接收、解析以及处理的各种状态信息呢,定义一个 HTTP 请求信息的结构用于填充吗?如果我们的服务器组件仅支持 HTTP 协议这样做是可以的,但我们设计的服务器的目标是要能够支持各种不同的应用层协议,便于我们组件的使用者能够根据自己不同的业务场景定制对应的应用层协议进行使用,因此我们就需要让这个结构能够保存不同类型的数据,此时就需要 any 出场了。 每一个Connection对连接进行管理,最终都不可避免需要涉及到应用层协议的处理,因此在Connection中需要设置协议处理的上下文来控制处理节奏。但是应用层协议千千万,为了降低耦合度,这个协议接收解析上下文就不能有明显的协议倾向,它可以是任意协议的上下文信息,因此就需要一个通用的类型来保存各种不同的数据结构。 在C语言中,通用类型可以使用void*来管理,但是在C++中,boost库和C++17给我们提供了一个通用类型any来灵活使用,如果考虑增加代码的移植性,尽量减少第三方库的依赖,则可以使用C++17特性中的any,或者自己来实现。而这个any通用类型类的实现其实并不复杂,以下是简单的部分实现。 下面是C++17中any的使用用例: 需要注意的是,C++17的特性需要高版本的g++编译器支持,建议g++ 7.3及以上版本。 基于以上的理解,我们要实现的是一个带有协议支持的Reactor模型高性能服务器,因此将整个项目的实现划分为两个大的模块: SERVER模块:实现Reactor模型的TCP服务器 协议模块:对当前的Reactor模型服务器提供应用层协议支持 SERVER模块就是对所有的连接以及线程进行管理,让它们各司其职,在合适的时候做合适的事,最终完成高性能服务器组件的实现。而具体的管理也分为三个方面: 监听连接管理:对监听连接进行管理。 通信连接管理:对通信连接进行管理。 超时连接管理:对超时连接进行管理。 基于以上的管理思想,将这个模块进行细致的划分又可以划分为以下多个子模块: Buffer 模块:实现通信套接字的用户态缓冲区,防止接收到的数据不是一条完整的数据,同时确保客户端响应的数据在套接字可写的情况下进行发送。 Socket 模块:对 socket 套接字的操作进行封装,使得程序中对于套接字的各项操作更加简便。 Channel 模块:对于一个描述符进行监控事件管理,便于在用户态对描述符的监控事件进行维护。 Connection 模块:对通信连接进行整体管理,一个连接的所有操作都通过此模块来完成,增加连接操作的灵活以及便捷性。 Acceptor 模块:对监听套接字进行管理,为客户端的新建连接创建 Connection 对象,并设置各种回调。 TimerQueue 模块:定时任务模块,让一个任务可以在指定的时间之后被执行。 Poller模块:对任意的描述符进行IO事件监控,本质上就是对 epoll 的各种操作进行封装,从而让对描述符进行事件监控的操作更加简单,此模块是 Channel 模块的一个子模块。 EventLoop 模块:对事件监控进行管理,为了确保线程安全,此模块一个模块对应一个线程,服务器中的所有的事件都是由此模块来完成。 LoopThread 模块:将 EventLoop 与 thread 整合到一起,向外部返回所实例化的 EventLoop 对象,即将 EventLoop 对象与线程一一绑定。 LoopThreadPool 模块:LoopThread 线程池,用于对所有的 LoopThread 进行管理及分配。 TcpServer 模块:对前边所有子模块进行整合,从而提供给组件使用者的可以便捷的完成一个高性能服务器搭建的模块。 Buffer模块是一个缓冲区模块,用于实现通信中用户态的接收缓冲区和发送缓冲区功能 功能:用于实现通信套接字的用户态缓冲区 意义: 1.防止接收到的数据不是一条完整的数据,因此对接收的数据进行缓存 2.对于客户端响应的数据,应该是在套接字可写的情况下进行发送 功能设计: 1.向缓冲区添加数据 2.从缓冲区中取出数据 Socket模块是对套接字操作封装的一个模块,主要实现的socket的各项操作。 功能:对socket套接字的操作进行封装 意义:程序中对于套接字的各项操作更加简便 功能设计: 1.创建套接字 2.绑定地址信息 3.开始监听 4.向服务器发起连接 5.获取新连接 6.接收数据 7.发送数据 8.创建一个监听连接 9.创建一个客户端连接 10.设置套接字选项–开启地址端口复用 11.设置套接字阻塞属性–设置为非阻塞 Channel模块是对一个描述符需要进行的IO事件管理的模块,实现对描述符可读,可写,错误事件的管理操作,以及Poller模块对描述符进行IO事件监控就绪后,根据不同的事件,回调不同的处理函数功能。 功能:对于一个描述符进行监控事件的管理 意义:对于描述符的监控事件在用户态更容易维护,以及触发事件后的操作流程更加的清晰 功能设计: 1.对监控事件的管理: 1.1描述符是否可读 1.2描述符是否可写 1.3对描述符监控可读 1.4对描述符监控可写 1.5解除对可读事件监控 1.6解除对可写事件监控 1.7解除所有事件监控 2.对监控事件触发后处理:设置对于不同事件的回调函数,明确触发了某个事件之后应该怎么处理 功能: 1.这是一个对于通信连接进行整体管理的一个模块。对一个连接的操作都是通过这个模块进行的 2.Connection模块,一个连接有任何的事件该怎么处理都是由这个模块来进行处理的,因为组件的设计也不知道使用者要如何处理事件。因此只能是提供一些事件回调函数由使用者设置 意义:这个模块本身来说不是一个单独的功能模块,是一个对连接做管理的模块。增加连接操作的灵活以及使捷性 功能设计: 1.关闭连接 2.发送数据 3.协议切换 4.启动非活跃连接超时释放 5.取消非活跃连接超时释放 6.回调函数设置: 1.连接建立完成的回调 2.连接有新数据接收成功后的回调 3.连接关闭时的回调 4.产生任何事件进行的回调 Connection模块是对Buffer模块,Socket模块,Channel模块的一个整体封装,实现了对一个通信套接字的整体的管理,每一个进行数据通信的套接字(也就是accept获取到的新连接)都会使用Connection进行管理。 Connection模块内部包含有四个由组件使用者传入的回调函数:连接建立完成回调,事件回调,新数据回调,关闭回调。 Connection模块内部包含有两个组件使用者提供的接口:数据发送接口,连接关闭接口 Connection模块内部包含有两个用户态缓冲区:用户态接收缓冲区,用户态发送缓冲区 Connection模块内部包含有一个Socket对象:完成描述符面向系统的IO操作 Connection模块内部包含有一个Channel对象:完成描述符IO事件就绪的处理 具体处理流程如下: 1.实现向Channel提供可读,可写,错误等不同事件的IO事件回调函数,然后将Channel和对应的描述符添加到Poller事件监控中。 2.当描述符在Poller模块中就绪了IO可读事件,则调用描述符对应Channel中保存的读事件处理函数,进行数据读取,将socket接收缓冲区全部读取到Connection管理的用户态接收缓冲区中。然后调用由组件使用者传入的新数据到来回调函数进行处理。 3.组件使用者进行数据的业务处理完毕后,通过Connection向使用者提供的数据发送接口,将数据写入Connection的发送缓冲区中。 4.启动描述符在Poll模块中的IO写事件监控,就绪后,调用Channel中保存的写事件处理函数,将发送缓冲区中的数据通过Socket进行面向系统的实际数据发送。 功能:对监听套接字进行管理 意义: 1.当获取了一个新建连接的描述符之后,需要为这个通信连接,封装一个Connection对象,设置各种不同回调 2.注意:因为Acceptor模块本身并不知道一个连接产生了某个事件该如何处理,因此获取一个通信连接后,Connection的封装,以及事件回调的设置都应该由服务器模块来进行 功能设计:回调函数设置,新建连接获取成功的回调设置,由服务器来指定 Acceptor模块是对Socket模块,Channel模块的一个整体封装,实现了对一个监听套接字的整体的管理。 Acceptor模块内部包含有一个Socket对象:实现监听套接字的操作 Acceptor模块内部包含有一个Channel对象:实现监听套接字IO事件就绪的处理 具体处理流程如下: 1.实现向Channel提供可读事件的IO事件处理回调函数,函数的功能其实也就是获取新连接 2.为新连接构建一个Connection对象出来。 功能:定时任务模块,让一个任务可以在指定的时间之后被执行 意义:组件内部,对于非活跃连接希望在N秒之后被释放 功能设计: 1.添加定时任务 2.刷新定时任务:希望一个定时任务重新开始计时 3.取消定时任务 TimerQueue模块是实现固定时间定时任务的模块,可以理解就是要给定时任务管理器,向定时任务管理器中添加一个任务,任务将在固定时间后被执行,同时也可以通过刷新定时任务来延迟任务的执行。这个模块主要是对Connection对象的生命周期管理,对非活跃连接进行超时后的释放功能。 TimerQueue模块内部包含有一个timerfd:Linux系统提供的定时器。 TimerQueue模块内部包含有一个Channel对象:实现对timerfd的IO时间就绪回调处理 功能:对任意的描述符进行lO事件监控 意义:对epoll进行的封装,让对描述符进行事件监控的操作更加简单 功能接口: 1.添加事件监控:Channel模块 2.修改事件监控 3.移除事件监控 Poller模块是对epoll进行封装的一个模块,主要实现epoll的IO事件添加,修改,移除,获取活跃连接功能。 功能: 1.进行事件监控管理的模块 2.这个模块其实就是我们所说的one thread one loop中的loop,也是我们所说的reactor 3.这个模块必然是一个模块对应一个线程 意义: 1.对于服务器中的所有的事件都是由EventLoop模块来完成 2.每一个Connection连接,都会绑定一个EventLoop模块和线程,因为外界对于连接的所有操作,都是要放到同一个线程中进行的 思想: 1.对所有的连接进行事件监控,连接触发事件后调用回调进行处理 2.对于连接的所有操作,都要放到EventLoop线程中执行 功能设计: 1.将连接的操作任务添加到任务队列 2.定时任务的添加 3.定时任务的刷新 4.定时任务的取消 EventLoop模块可以理解就是我们上边所说的Reactor模块,它是对Poller模块,TimerQueue模块,Socket模块的一个整体封装,进行所有描述符的事件监控。EventLoop模块必然是一个对象对应一个线程的模块,线程内部的目的就是运行EventLoop的启动函数。 EventLoop模块为了保证整个服务器的线程安全问题,因此要求使用者对于Connection的所有操作一定要在其对应的EventLoop线程内完成,不能在其他线程中进行(比如组件使用者使用Connection发送数据,以及关闭连接这种操作)。 EventLoop模块保证自己内部所监控的所有描述符,都要是活跃连接,非活跃连接就要及时释放避免资源浪费。 EventLoop模块内部包含有一个eventfd:eventfd其实就是Linux内核提供的一个事件fd,专门用于事件通知。 EventLoop模块内部包含有一个Poller对象:用于进行描述符的IO事件监控。 EventLoop模块内部包含有一个TimerQueue对象:用于进行定时任务的管理。 EventLoop模块内部包含有一个PendingTask队列:组件使用者将对Connection进行的所有操作,都加入到任务队列中,由EventLoop模块进行管理,并在EventLoop对应的线程中进行执行。 每一个Connection对象都会绑定到一个EventLoop上,这样能保证对这个连接的所有操作都是在一个线程中完成的。 具体操作流程: 1.通过Poller模块对当前模块管理内的所有描述符进行IO事件监控,有描述符事件就绪后,通过描述符对应的Channel进行事件处理。 2.所有就绪的描述符IO事件处理完毕后,对任务队列中的所有操作顺序进行执行。 3.由于epoll的事件监控,有可能会因为没有事件到来而持续阻塞,导致任务队列中的任务不能及时得到执行,因此创建了eventfd,添加到Poller的事件监控中,用于实现每次向任务队列添加任务的时候,通过向eventfd写入数据来唤醒epoll的阻塞。 功能:对前边所有子模块的整合模块,是提供给用户用于搭建一个高性能服务器的模块 意义:让组件使用者可以更加轻使的完成—个服务器的搭建 功能设计: 1.对于监听连接的管理 2.对于通信连接的管理 3.对于超时连接的管理 4.对于事件监控的管理 5.事件回调函数的设置:一个连接产生了一个事件,对于这个事件如何处理,只有组件使用者知道,因此一个事件的处理回调,一定是组件使用者,设置给TcpServer,TcpServer设置给各个Connection连接 这个模块是一个整体TCP服务器模块的封装,内部封装了Acceptor模块,EventLoop ThreadPool模块。 TcpServer中包含有一个EventLoop对象:以备在超轻量使用场景中不需要EventLoop线程池,只需要在主线程中完成所有操作的情况。 TcpServer模块内部包含有一个EventLoop ThreadPool对象:其实就是EventLoop线程池,也就是子Reactor线程池 TcpServer模块内部包含有一个Acceptor对象:一个TcpServer服务器,必然对应有一个监听套接字,能够完成获取客户端新连接,并处理的任务。 TcpServer模块内部包含有一个std::shared_ptr的hash表:保存了所有的新建连接对应的Connection,注意,所有的Connection使用shared_ptr进行管理,这样能够保证在hash表中删除了Connection信息后,在shared_ptr计数器为0的情况下完成对Connection资源的释放操作。 具体操作流程如下: 1.在实例化TcpServer对象过程中,完成BaseLoop的设置,Acceptor对象的实例化,以及EventLoop线程池的实例化,以及std::shared_ptr的hash表的实例化。 2.为Acceptor对象设置回调函数:获取到新连接后,为新连接构建Connection对象,设置Connection的各项回调,并使用shared_ptr进行管理,并添加到hash表中进行管理,并为Connection选择一个EventLoop线程,为Connection添加一个定时销毁任务,为Connection添加事件监控, 3.启动BaseLoop。 HTTP协议模块用于对高并发服务器模块进行协议支持,基于提供的协议支持能够更方便的完成指定协议服务器的搭建。而HTTP协议支持模块的实现,可以细分为以下几个模块。 这个模块是一个工具模块,主要提供HTTP协议模块所用到的一些工具函数,比如url编解码,文件读写等。 这个模块是HTTP请求数据模块,用于保存HTTP请求数据被解析后的各项请求元素信息。 这个模块是HTTP响应数据模块,用于业务处理后设置并保存HTTP响应数据的的各项元素信息,最终会被按照HTTP协议响应格式组织成为响应信息发送给客户端。 这个模块是一个HTTP请求接收的上下文模块,主要是为了防止在一次接收的数据中,不是一个完整的HTTP请求,则解析过程并未完成,无法进行完整的请求处理,需要在下次接收到新数据后继续根据上下文进行解析,最终得到一个HttpRequest请求信息对象,因此在请求数据的接收以及解析部分需要一个上下文来进行控制接收和处理节奏。 这个模块是最终给组件使用者提供的HTTP服务器模块了,用于以简单的接口实现HTTP服务器的搭建。 HttpServer模块内部包含有一个TcpServer对象:TcpServer对象实现服务器的搭建 HttpServer模块内部包含有两个提供给TcpServer对象的接口:连接建立成功设置上下文接口,数据处理接口。 HttpServer模块内部包含有一个hash-map表存储请求与处理函数的映射表:组件使用者向HttpServer设置哪些请求应该使用哪些函数进行处理,等TcpServer收到对应的请求就会使用对应的函数进行处理。 整体的模块示意图如下: Connection 模块关系图,Acceptor 模块关系图,EventLoop 模块关系图 Buffer模块:缓冲区模块 提供的功能:存储数据,取出数据 实现思想: 1.实现缓冲区得有一块存储空间,采用vector vector底层其实使用的就是一块线性的空间 2.要素: 1.默认空间的大小 2.当前的读取数据位置 3.当前的写入数据位置 3.操作: 1.写入数据:当前写入位置指向哪里,就从哪里开始写入,如果后续剩余的空间不够了,考虑整体缓冲区空间是否足够(因为读位置也会向后偏移,前边有可能会有空闲空间)如果空间足够,将数据移动到起始位置即可,如果空间不够,就进行扩容,从当前写位置开始扩容足够空间大小,数据一旦写入成功,当前写位置就要向后偏移 2.读取数据:当前的读取位置指向哪里,就从哪里开始读取,前提是有数据可读,可读数据大小:当前写入位置减去当前读取位置 Buffer 模块的设计思想如下: 框架设计: 具体实现: 功能设计: 1.创建套接字 2.绑定地址信息 3.开始监听 4.向服务器发起连接 5.获取新连接 6.接收数据 7.发送数据 8.创建一个监听连接 9.创建一个客户端连接 10.设置套接字选项–开启地址端口复用 11.设置套接字阻塞属性–设置为非阻塞 具体实现时的一些细节如下: 具体实现: Channel类设计 目的:对描述符的监控事件管理 1.事件管理: 描述符是否可读 描述符是否可写 对描述符监控可写 对描述符监控可读 解除可写事件监控 解除可读事件监控 2.事件触发后的处理的管理 1.需要处理的事件:可读,可写,挂断,错误,任意 2.事件处理的回调函数 具体实现时的一些细节如下: 以上的事件都是使用一个数值uint32_t 进行保存 要进行事件管理,就需要有一个uint32_t 类型的成员保存当前需要监控的事件 事件处理这里,因为有五种事件需要处理,就需要五个回调函数 主要框架: 具体实现: Poller模块:描述符IO事件监控模块 意义:通过epoll实现对描述符的 IO 事件监控 功能: 1.添加/修改描述符的事件监控(不存在则添加,存在则修改) 2.移除描述符的事件监控 封装思想: 1.必须拥有一个epoll的操作句柄 2.拥有一个struct epoll_event 结构数组,监控时保存所有的活跃事件 3.使用hash表管理描述符与描述符对应的事件管理Channel事件 逻辑流程: 1.对描述符进行监控,通过Channel才知道描述符需要监控什么事件 2.当描述符就绪了,通过描述符在hash表中找到对应的Channel(得到了Channel才能知道什么事件如何处理)当描述符就绪了,返回描述符对应的Channel 具体实现时的一些细节如下: 主要框架: 具体实现: eventfd:一种事件通知机制 创建一个描述符用于实现事件通知,eventfd本质在内核中管理的就是一个计数器,创建eventfd就会在内核中创建一个计数器(结构),每当eventfd中写入一个数值–用于表示事件通知次数,可以使用read进行数据的读取,读取到的数据就是通知的次数,假设每次给eventfd中写入一个1,就表示通知了一次,连续写了三次之后,再去read读取出来的数字就是3,读取之后计数清0。 用处:在EventLoop模块中实现线程间事件通知功能 使用案例: EventLoop:进行事件监控以及事件处理的模块 关键点:这个模块与线程是一一对应关联的 监控了一个连接,而这个连接一旦就绪,就要进行事件处理,但是如果这个描述符,在多个线程中都触发了事件,进行处理,就会存在线程安全问题,因此我们需要将一个连接的事件监控,以及连接事件处理,以及其他操作都放在一个线程中进行 如何保证一个连接的所有操作都在EventLoop对应的线程中,解决方案:给EventLoop模块中,添加一个任务队列,对连接的所有操作,都进行一次封装,将对连接的操作并不直接执行,而是当做任务添加到任务队列中 EventLoop处理流程: 1.在线程中对描述符进行事件监控 2.有描述符就绪则对描述符进行事件处理(如何保证处理回调函数中的操作都在线程中) 3.所有的就绪事件处理完了,这个时候再去将任务队列中的所有任务一一执行 EventLoop分为epoll和task任务队列。epoll中文件描述符就绪了,进行事件处理–调用回调函数,处理过程中调用了send,而这个send是封装后的send,实际上内部是将数据的发送操作,压入队列,等到所有的就绪事件都处理完了,然后从task任务队列中一 一取出实际要进行操作执行。这样能够保证对于连接的所有操作,都是在一个线程中进行的,不涉及线程安全问题,但是对于任务队列的操作有线程安全问题,只需要给task的操作加上一把锁即可。 数据: 1.事件监控:即Poller模块,有事件就绪则进行事件处理 2.执行任务队列中的任务:一个线程安全的任务队列 注意点:因为有可能因为等待描述符IO事件就绪,导致执行流阻塞,这时候任务队列中的任务将得不到执行,因此得有一个事件通知的东西,能够唤醒事件监控的阻塞 当事件就绪,需要处理的时候,处理过程中,如果对连接要进行某些操作:这些操作必须在EventLoop对应的线程中执行,保证对连接的各项操作都是线程安全的。 1.如果执行的操作本就在线程中,不需要将操作压入队列了,可以直接执行 2.如果执行的操作不在线程中,才需要加入任务池,等待事件处理完了然后执行任务 具体实现时的一些细节如下: 定时器模块的整合: timerfd:实现内核每个一段时间,给进程一次超时时间(timerfd可读) timewheel:实现每次执行Runtimetask,都可以执行一波到期的定时任务,要实现一个完整的秒级定时器,就需要将这两个功能整合到一起。 timerfd设置每秒钟触发一次定时事件,当事件被触发,则运行一次timerwheel的runtimertask,执行一下所有的过期定时任务 具体实现时的一些细节如下: timewheel模块代码 EventLoop类的实现: Connection: 目的:对连接进行全方位的管理,对通信连接的所有操作都是通过这个模块提供的功能完成 管理: 2.连接事件的管理,可读,可写,错误,挂断,任意 3.缓冲区的管理,便于socket数据的接收和发送 4.协议上下文的管理,记录请求数据的处理过程 5.回调函数的管理 因为连接接收到数据之后该如何处理,需要由用户决定,因此必须有业务处理回调函数 一个连接建立成功后,该如何处理,由用户决定,因此必须有连接建立成功的回调函数 一个连接关闭前,该如何处理,由用户决定,因此必须由关闭连接回调函数。 任意事件的产生,有没有某些处理,由用户决定,因此必须有任意事件的回调函数 功能: 2关闭连接—给用户提供的关闭连接接口,应该在实际释放连接之前,看看输入输出缓冲区是否有数据待处理 3.启动非活跃连接的超时销毁功能 4.取消非活跃连接的超时销毁功能 5.协议切换-一个连接接收数据后如何进行业务处理,取决于上下文,以及数据的业务处理回调函数 Connection模块是对连接的管理模块,对于连接的所有操作都是通过这个模块完成的 场景:对连接进行操作的时候,但是连接已经被释放,导致内存访问错误,最终程序崩溃 解决方案:使用智能指针shared_ptr对Connection对象进行管理,这样就能保证任意一个地方对Connection对象进行操作的时候,保存了一份shared_ptr,因此就算其他地方进行释放操作,也只是对shared_ptr的计数器-1.而不会导致Connection的实际释放 具体实现时的一些细节如下: 完整代码: Acceptor模块:对监听套接字进行管理 1.创建一个监听套接字 2.启动读事件监控 3.事件触发后,获取新连接 4.调用新连接获取成功之后的回调函数 为新连接创建Connection进行管理(这一步不是Acceptor模块的操作,应该是服务器模块) 因为Acceptor模块只进行监听连接的管理,因此获取新连接的描述符之后,对于新连接描述符如何处理其实并不关心 对于新连接如何处理,应该服务器模块来管理的 服务器模块,实现了一个对于新连接描述符处理的函数,将这个函数设置给Acceptor模块中的回调函数 实现时的一些细节如下: 完整代码: 目标:将EventLoop模块与线程整合起来 EventLoop模块与线程是一一对应的 EventLoop模块实例化的对象,在构造的时候就会初始化_thread_id 而后边当运行一个操作的时候判断当前是否运行EventLoop模块对应的线程中,就是将线程ID与EventLoop中的_thread_id进行一个比较,相同就表示同一个线程,不同就表示当前运行的并不是EventLoop线程 含义:EventLoop模块在实例化对象的时候,必须在线程的内部 EventLoop实例化对象时会设置自己的_thread_id 如果我们先创建了多个EventLoop对象,再设置新的_thread_id期间是不可控的 因此我们必须先创建线程,然后在线程的入口函数中,去实例化EventLoop对象 构造一个新的模块:LoopThread 这个模块的功能:将EventLoop与Thread整合到一起 思想: 1.创建线程 2.在线程中实例化EventLoop对象 功能:可以向外部返回实例化的EventLoop 我们上面在设计 EventLoop 模块时提到 EventLoop 模块与线程是一一对应的,并且由于 EventLoop 模块在构造时就会使用当前线程 id 来作为 EventLoop 对象所关联的线程的 id – _thread_id(std::this_thread::get_id());同时,我们后面在运行一个操作的时候判断当前是否运行在 EventLoop 模块对应的线程中,就是将线程 ID 与 EventLoop 模块中的 _thread id 进行比较,相同表示在同一个线程,不同则表示当前运行线程并不是 EventLoop 线程。 因此,EventLoop 模块必须在线程内部实例化,即先为 EventLoop 对象创建一个线程,然后在该线程的入口函数中去实例化 EventLoop 对象,这样该线程就会与 EventLoop 对象相关联 (实例化时该线程 id 被用于初始化 EventLoop 对象的 _thread_id)。 需要注意的是,我们不能事先创建多个 EventLoop 对象,然后创建多个线程,最后将各个线程的 id 重新赋值给 EventLoop 进行关联,因为这样在构造 EventLoop 对象到设置新的 _thread_id 期间,EventLoop 产生的操作将是不可控的。 基于以上思想,我们需要构建一个 LoopThread 模块,这个模块的功能是将 EventLoop 与 thread 整合到一起,向外部返回所实例化的 EventLoop 对象。 代码实现: LoopThreadPool针对LoopThread设计一个线程池 LoopThreadPool模块:对所有的LoopThread进行管理和分配 功能: 1.线程数量可配置(0个或多个) 注意事项:在服务器中,主从Reactor模型是主线程只负责新连接获取,从属Reactor负责线连接的事件监控及业务处理,因此当前的线程池,有可能从属线程数量为0,也就是实现单Reactor服务器,一个线程既负责获取新连接,也负责连接到处理 2.对所有的线程进行管理,其实就是管理0个或多个LoopThread对象 3.提供线程分配的功能: 当主线程获取了一个新连接,需要将新连接挂到从属线程进行事件监控及处理 假设有0个从属线程,则直接分配给主线程的EventLoop,进行处理。 假设有多个从属线程,则采用RR轮转思想,进行线程的分配(将对应的EventLoop获取到,设置对应的Connection) 我们上面针对 EventLoop 设计 LoopThread 模块,由于客户端连接有多个,而每一个客户端连接都对应一个 Connection 模块、EventLoop 模块以及 LoopThread 模块,因此我们需要针对 LoopThread 设计一个线程池 – LoopThreadPool,用于对所有的 LoopThread 进行管理及分配。 LoopThreadPool 模块所要完成的功能如下: 线程数量可配置 (0个或多个)。 需要注意的是,在服务器中,由于主从 Reactor 模型是主线程只负责新连接获取,从属线程负责新连接的事件监控及处理,因此当前的线程池中从属线程的数量有可能会为0,也就是实现单 Reactor 服务器,仅有一个线程,其即负责获取连接,也负责连接的处理。 对所有的线程进行管理 – 管理0个或多个 LoopThread 对象. 提供线程分配的功能 – 当主线程获取了一个新连接时,将新连接挂到从属线程上进行事件监控及处理。 假设有0个从属线程,则直接分配给主线程的 EventLoop 进行处理;假设有多个从属线程,则采用 RR 轮转思想,进行线程的分配 (将被选择线程的 EventLoop 对象获取到,然后设置给对应的 Connection 对象) 完整代码: TcpServer模块:对于所有模块的整合,通过TcpServer模块实例化的对象,可以非常简单的实现一个服务器的搭建 管理: 1.Acceptor对象,创建一个监听套接字 2.EventLoop对象,baseloop对象,实现对监听套接字的事件监控 3.std::unordered_map 4.LoopThreadLoop对象,创建loop线程池,对新建连接进行事件监控及处理 功能: 1.设置从属线程池数量 2.启动服务器 3.设置各种回调函数(连接建立完成,消息,关闭,任意),用户设置给TcpServer,TcpServer设置给获取的新连接 4.是否启动非活跃连接超时销毁功能 5.添加定时任务功能 流程: 1.在TcpServer中实例化一个Acceptot对象,以及一个EventLoop对象(baseloop) 2.将Acceptor挂到baseloop上进行事件监控 3.一旦Acceptor对象就绪了可读事件,则执行可读事件回调函数获取新建连接 4.对新连接,创建一个Connection进行管理 5.对连接对应的Connection设置功能回调(连接完成回调,消息回调,关闭回调,任意事件回调) 6.启动Connection的非活跃连接的超时销毁规则 7.将新连接对应的Connection挂到LoopThreadPool中的从属线程对应的EventLoop中进行事件监控 8.一旦Connection对应的连接就绪了可读事件,则这时候执行事件回调函数,读取数据,读取完毕后调用TcpServer设置的消息回调函数 完整代码: EchoServer.hpp tcpClient.cc main.cc 在Util工具类中主要实现一下的功能: 1.读取文件内容 2.向文件写入数据 3.URL编码 在RFC3986文档中规定的URL绝对不编码字符:. - _ ~以及数字和字母 还有一个就是在不同的一些标准中的特殊处理 W3C标准中规定param中的空格必须被编码为+ REF 2396中规定URL中保留字符需要转换为%HH格式 4.URL解码 5.响应状态码描述的获取 6.根据文件后缀名获取文件mime 7.判断一个文件是否是目录 8.判断一个文件是否是一个普通的文件 9.http请求的资源路径有效性判断 代码实现: HttpRequest模块: Http请求信息模块:存储http请求信息要素,提供简单的功能性接口 请求信息要素: 请求行:请求方法 URL 协议版本 URL:资源路径 查询字符串 GET /search/1234?word=C++&en=utf8 HTTP/1.1 请求头部:key:value
key:value
… Content-Length:0
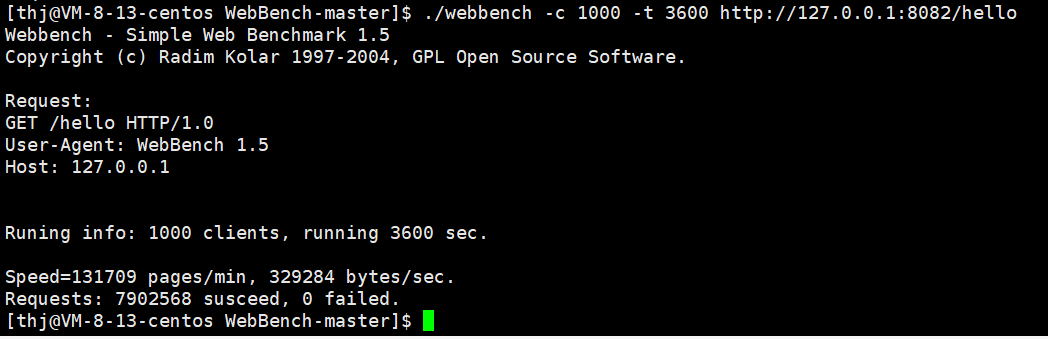
正文 要素:请求方法,资源路径,查询字符串,头部字段,正文,协议版本 std::smatch 保存首行使用regex正则进行解析后,所提取的数据,比如提取资源路径中的数字 代码实现: HttpResponse模块: 功能:存储http响应信息要素,提供简单的功能性接口 响应信息要素: 1.响应状态码 2.头部字段 3.响应正文 4.重定向信息(是否进行了重定向的标志,重定向的路径) 功能性接口: 0.为了便于成员的访问,因此将成员设置为共有成员 1.头部字段的新增,查询,获取 2.正文的设置 3.重定向的设置 4.长短连接的判断 代码实现: 代码实现: HttpServer模块:用于实现HTTP服务器的搭建 设计一张请求路由表: 表中记录了针对哪个请求,应该使用哪个函数来进行业务处理的映射关系 当服务器收到了一个请求,就在请求路由表中,查找有没有对应请求的处理函数,如果有,则执行对应的处理函数即可说白了,什么请求,怎么处理,由用户来设定,服务器收到了请求只需要执行函数即可 这样做的好处:用户只需要实现业务处理函数,然后将请求与处理函数的映射关系,添加到服务器中 而服务器只需要接收数据,解析数据,查找路由表映射关系,执行业务处理函数。 要实现简便的搭建HTTP服务器,所需要的要素和提供的功能要素: 1.GET请求的路由映射表 2.POST请求的路由映射表 3.PUT请求的路由映射表 4.DELETE请求的路由映射表﹐—路由映射表记录对应请求方法的请求的处理函数映射关系—更多是功能性请求的处理 5.静态资源相对根目录—实现静态资源请求的处理 6.高性能TCP服务器—进行连接的IO操作 接口: 服务器处理流程: 1.从socket接收数据,放到接收缓冲区 2.调用OnMessage回调函数进行业务处理 3.对请求进行解析,得到了一个HttpRequest结构,包含了所有的请求要素 4.进行请求的路由查找–找到对应请求的处理方法 1.静态资源请求—一些实体文件资源的请求,html,image… 将静态资源文件的数据读取出来,填充到HttpResponse结构中 2.功能性请求—在请求路由映射表中查找处理函数,找到了则执行函数 具体的业务处理,并进行HttpResponse结构的数据填充 5.对静态资源请求/功能性请求进行处理完毕后,得到了一个填充了响应信息的HttpResponse对象,组织http格式响应,进行发送 接口: 添加请求-处理函数映射信息(GET/POST/PUT/DELETE)设置静态资源根目录 设置是否启动超时连接关闭 设置线程池中线程数量启动服务器 OnConnected —用于给TcpServer设置协议上下文 OnMessage -----用于进行缓冲区数据解析处理 获取上下文,进行缓冲区数据解析 请求的路由查找 静态资源请求查找和处理功能性请求的查找和处理组织响应进行回复 HTTP 服务器的运行流程如下: 代码实现: 下面我们分别对 HttpServer 的 GPT、POST、PUT 以及 DELETE 请求进行简单测试。 测试代码如下: 项目目录结构如下: 静态资源根目录中的文件信息如下: 回显服务器测试结果如下: 登录请求测试结果如下: 面我们已经完成了 SERVER 模块和协议模块的开发,并进行了简单的功能测试,下面我们来进行一些边界性的功能测试,观察服务器在边界情况下能够正常运行。 创建一个客户端,设置 Connection 头部字段为 keep-alive,观察客户端是否能够持续与服务器进行通信。 从测试结果可以看到,客户端能够持续与服务器进行通信,并且服务器也不会在 10s 后将客户端连接释放,而是等待客户端主动退出后才会释放: 过几分钟之后再关闭客户端 客户端收到的响应 客户端连接上服务器后,长时间不给服务器发送数据,观察超时时间 (10s) 后服务器是否会将客户端连接进行释放。 从测试结果可以看到,服务器经过超时时间后自动将客户端连接释放: 给服务器发送一个请求,添加头部字段 Content-Length 为100,但实际发送的正文长度不足100,观察服务器的处理结果;我们的预期结果有两种: 测试代码 测试结果如下: 当服务器达到性能瓶颈,即处理一次业务花费的时间超过了服务器设置的非活跃连接超时时间时,查看服务器的处理情况。我们的预期结果如下: 测试结果如下: 客户端一次性给服务器发送多条请求,观察服务器处理结果。 测试结果如下,服务器能够正常处理并响应: 使用PUT方法向服务器传输大文件,观察服务器处理结果。 服务器内存情况以及 test.txt 文件情况如下: 测试结果如下,服务器能够正常处理并响应: 由于服务器资源有限,只能上传100M数据 使用服务器压力测试工具 WebBench 模拟多个客户端同时访问服务器,测试服务器的并发量 (可以同时处理多少个客户端的请求而不会出现连接失败) 以及 QPS (每秒钟处理的包的数量)。 测试环境如下: 测试结果如下 ( 2000 QPS ): 当服务器达到性能瓶颈,即处理一次业务花费的时间超过了服务器设置的非活跃连接超时时间时,查看服务器的处理情况。我们的预期结果如下: 测试结果如下: 客户端一次性给服务器发送多条请求,观察服务器处理结果。 测试结果如下,服务器能够正常处理并响应: 使用PUT方法向服务器传输大文件,观察服务器处理结果。 服务器内存情况以及 test.txt 文件情况如下: 测试结果如下,服务器能够正常处理并响应: 由于服务器资源有限,只能上传100M数据 使用服务器压力测试工具 WebBench 模拟多个客户端同时访问服务器,测试服务器的并发量 (可以同时处理多少个客户端的请求而不会出现连接失败) 以及 QPS (每秒钟处理的包的数量)。 测试环境如下: 测试结果如下 ( 2000 QPS ):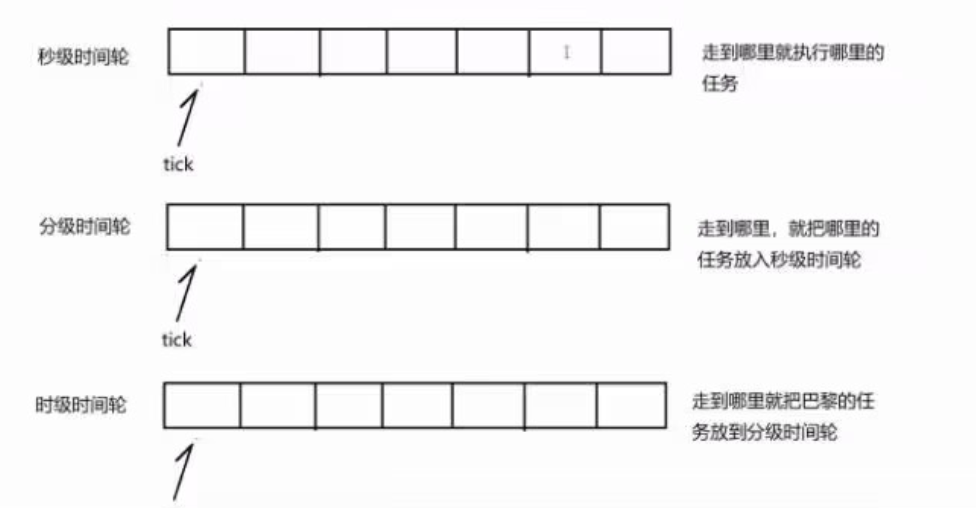
int *a = new int;
std:shared ptr<int> pi(a); --- a对象只有在pi计数为0的时候,才会被释放
std:shared ptr<int> pi1(pi) --当针对pi又构建了一个shared_ptr对象,则pi和pi1计数器为2
#include 3.正则库的简单使用
bool std:regex_match (const stdrstring &src, std:smatch &matches, std:regex &e)
src:原始字符串
matches: 正则表达式可以从原始字符串中匹配并提取符合某种规则的数据,提取的数据就放在matches中,是一个类似于数组的容器
e: 正则表达式的匹配规则
返回值:用于确定匹配是否成功
void regex_test()
{
std::string str = "/numbers/1234";
// 匹配以 /numbers/ 为起始位置,后面跟一个或多个数字字符的字符串
// 并且在匹配的过程中提取这个匹配到的数字字符串
std::regex e("/numbers/(d+)");
std::smatch matches;
bool ret = std::regex_match(str, matches, e);
if (ret == false)
{
std::cout << "regex_match failed" << std::endl;
}
for (auto &str : matches)
{
std::cout << str << std::endl;
}
}
// 输出结果
/numbers/1234
1234
int main()
{
// HTTP请求行格式: GET /www.baidu.com/login?user=xiaoming&pass=123123 HTTP/1.1
std::string request = "GET /www.baidu.com/login?user=xiaoming&pass=123123 HTTP/1.1
";
std::smatch matches;
// 请求方法的匹配 GET HEAD POST PUT DELETE
// GET|HEAD|POST|PUT|DELETE 表示匹配并提取其中的任意一个字符串
// [^?*] 表示匹配非问号字符 后边的*表示0次或多次
// ?(.*) ? 表示原始的 ? 到字符,(.*)表示提取问哈之后的任意字符0次或多次,直到遇空格
// HTTP/1.[01] 表示匹配以 HTTP/1.开始,后边有个0或1的字符串
std::regex e("(GET|HEAD|POST|PUT|DELETE) ([^?]*)(?:?(.*))? (HTTP/1.[01])(?:
|
)?");
// (?:
|
)? (?:...)表示匹配某个格式的字符串,但是不提取
// 最后的?表示的是匹配前面的表达式0次或者1次
bool ret = std::regex_match(request, matches, e);
if (ret == false)
{
std::cout << "regex_match failed" << std::endl;
}
for (auto &str : matches)
{
std::cout << str << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
4.通用类型any类型的实现
#include int main()
{
std::any a;
a = 10;
int *pi = std::any_cast<int>(&a);
std::cout << *pi << std::endl;
a = std::string("hello");
std::string *ps = std::any_cast<std::string>(&a);
std::cout << *ps << std::endl;
}
sudo yum install centos-release-scl-rh centos-release-scl
sudo yum install devtoolset-7-gcc devtoolset-7-gcc-c++
source /opt/rh/devtoolset-7/enable
echo "source /opt/rh/devtoolset-7/enable" >> ~/.bashrc
// 查看g++版本
g++ -v
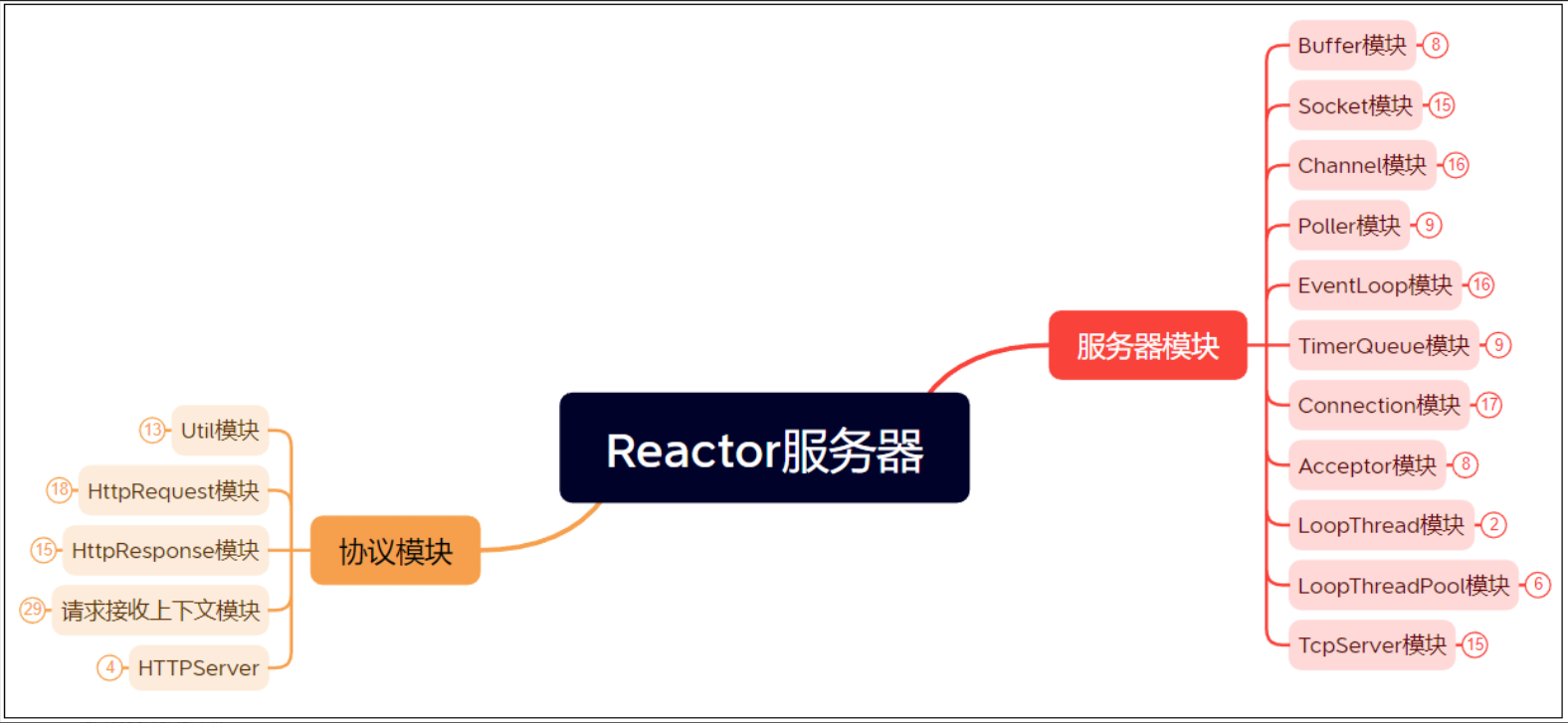
四、功能模块划分
1.SERVER模块
1.1Buffer模块
1.2.Socket模块
1.3Channel模块
1.4Connection模块
1.5Acceptor模块
1.6TimerQueue模块
1.7Poller模块
1.8EventLoop模块
1.9TcpServer模块
2.HTTP协议模块
2.1Util模块
2.2HttpRequest模块
2.3HttpResponse模块
2.4HttpContext模块
2.5HttpServer模块
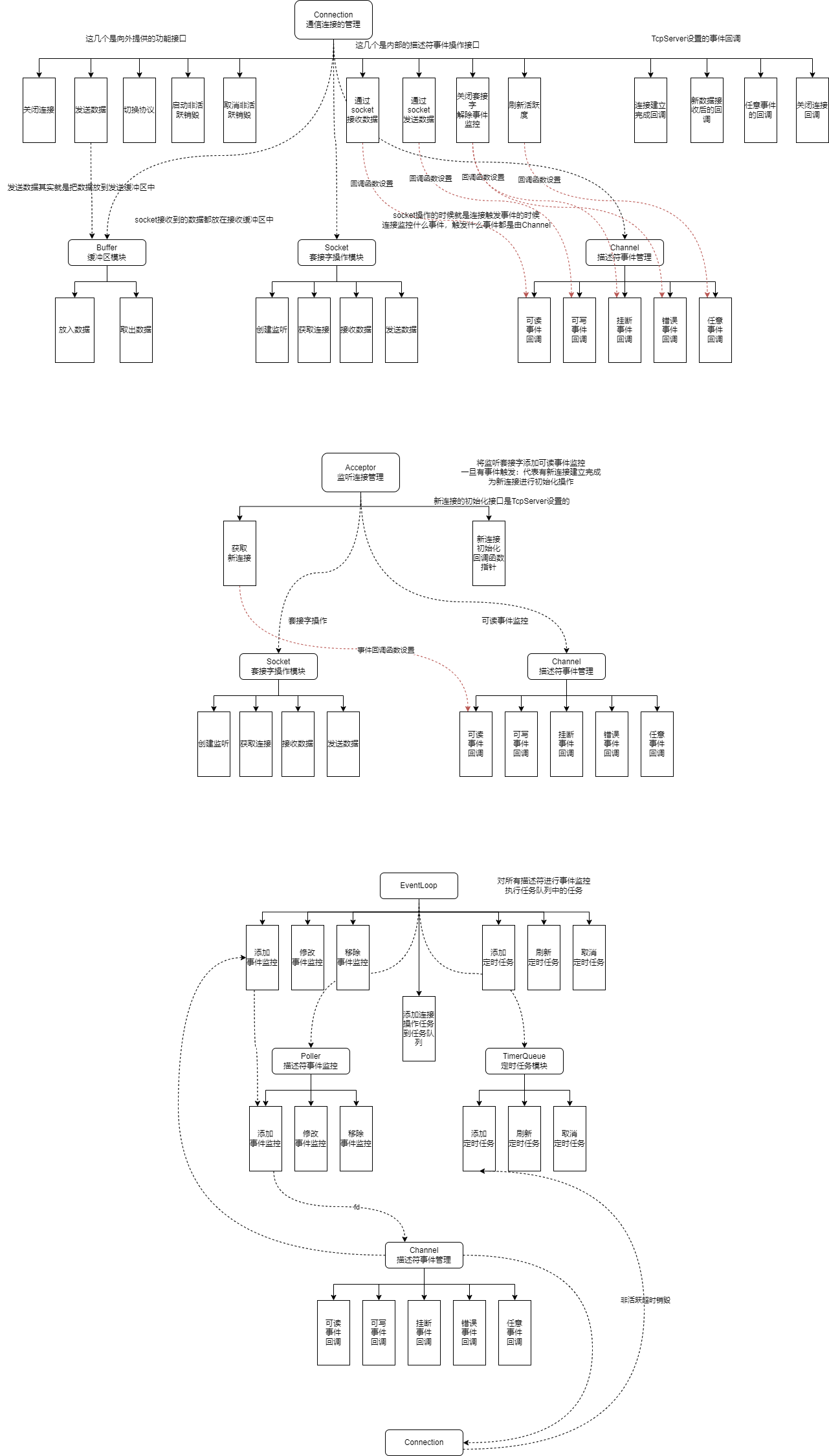
五、模块关系图
六、SERVER服务器模块实现
1.缓冲区Buffer类实现

class Buffer
{
private:
std::vector<char> _buffer;
/*位置是一个相对偏移量,而不是绝对地址*/
uint64_t _read_index;// 读位置
uint64_t _write_index;// 写位置
public:
// 1.获取当前写位置地址
// 2.确保可写空间足够(移动+扩容)
// 3.获取前沿空闲空间大小
// 4.获取后沿空闲空间大小
// 5.将写位置向后移动指定长度
// 6.获取当前读位置地址
// 7.获取可读数据大小
// 8.将读位置向后移动指定长度
// 9.清理功能
};
#define BUFFER_DEFAULT_SIZE 1024
class Buffer
{
private:
std::vector<char> _buffer; // 使用vector进行内存空间管理
uint64_t _reader_idx; // 读偏移
uint64_t _writer_idx; // 写偏移
public:
Buffer() : _reader_idx(0), _writer_idx(0), _buffer(BUFFER_DEFAULT_SIZE) {}
~Buffer() {}
public:
// 获取起始地址
char *Begin() { return &*_buffer.begin(); }
// 获取当前写入起始位置 _buffer的空间起始地址加上写偏移量
char *WritePosition() { return Begin() + _writer_idx; }
// 获取当前读物起始位置
char *ReadPosition() { return Begin() + _reader_idx; }
// 获取前沿空闲空间大小(缓冲区末尾)--写偏移之后的空闲空间,总体空间大小减去写偏移
uint64_t TailIdleSize() { return _buffer.size() - _writer_idx; }
// 获取后沿空闲空间大小(缓冲区起始)--读偏移之前的空闲空间--读偏移之前的空闲空间
uint64_t HeadIdleSize() { return _reader_idx; }
// 获取可读数据大小 写偏移-读偏移
uint64_t ReadAbleSize() { return _writer_idx - _reader_idx; }
// 将读偏移向后移动
void MoveReadOffset(const uint64_t &len)
{
if (len == 0)
return;
// 读偏移向后移动的大小,必须小于可读数据大小
assert(len <= ReadAbleSize());
_reader_idx += len;
}
// 将写偏移向后移动
void MoveWriteOffset(const uint64_t &len)
{
if (len == 0)
return;
// 写偏移向后移动的大小,必须小于后边的空闲空间大小
assert(len <= TailIdleSize());
_writer_idx += len;
}
// 确保可写空间足够(整体空间足够了就一定数据,否则就扩容)
void EnsureWriteSpace(const uint64_t &len)
{
// 1.如果末尾空闲空间大小足够,直接返回
if (len <= TailIdleSize())
{
return;
}
// 2.末尾空闲空间不够,则判断加上起始空闲空间大小是否足够,足够就将数据移动到起始位置
else if (len <= TailIdleSize() + HeadIdleSize())
{
// 将数据移动到起始位置
uint64_t readablesize = ReadAbleSize(); // 把当前数据大小先保存起来
// 将数据拷贝到起始位置
// std::copy(ReadPosition(),WritePosition(),Begin());
std::copy(ReadPosition(), ReadPosition() + readablesize, Begin());
_reader_idx = 0; // 将读偏移归0
_writer_idx = readablesize; // 将写位置置为可读数据大小
}
// 3.总体空间不够,则需要扩容,不移动数据,直接给写偏移之后扩容足够空间即可
else
{
_buffer.resize(_writer_idx + len);
}
}
// 写入数据
void Write(const void *buffer, const uint64_t &len)
{
// 1.保证有足够的空间 2.将数据拷贝进去
if (len == 0)
return;
EnsureWriteSpace(len);
const char *d = (const char *)buffer;
std::copy(d, d + len, WritePosition());
}
// 写入数据并且写偏移向后移动
void WriteAndPush(const void *buffer, const uint64_t &len)
{
Write(buffer, len);
MoveWriteOffset(len);
}
// 写入字符串
void WriteString(std::string &data)
{
// return Write(&data[0], data.size());
return Write(data.c_str(), data.size());
}
// 写入字符串并且写偏移向后移动
void WriteStringAndPush(std::string &data)
{
WriteString(data);
MoveWriteOffset(data.size());
}
// 写入一个Buffer对象
void WriteBuffer(Buffer &data)
{
return Write(data.ReadPosition(), data.ReadAbleSize());
}
void WriteBufferAndPush(Buffer &data)
{
WriteBuffer(data);
MoveWriteOffset(data.ReadAbleSize());
}
// 读取数据
void Read(void *buffer, const uint64_t &len)
{
// 要求要获取的数据大小必须小于可读数据大小
assert(len <= ReadAbleSize());
std::copy(ReadPosition(), ReadPosition() + len, (char *)buffer);
}
// 读取数据并读偏移向后移动
void ReadAndPop(void *buffer, const uint64_t &len)
{
Read(buffer, len);
MoveReadOffset(len);
}
// 读取数据放入一个字符串中
std::string ReadAsString(const uint64_t &len)
{
// 要求要获取的数据大小必须小于可读数据大小
assert(len <= ReadAbleSize());
std::string str;
str.resize(len);
Read(&str[0], len);
return str;
}
std::string ReadAsStringAndPop(const uint64_t &len)
{
assert(len <= ReadAbleSize());
std::string str = ReadAsString(len);
MoveReadOffset(len);
return str;
}
// 找到换行字符
char *FindCRLF()
{
char *res = (char *)memchr(ReadPosition(), '
', ReadAbleSize());
return res;
}
// 获取一行数据
std::string GetOneLine()
{
char *pos = FindCRLF();
if (pos == nullptr)
return "";
// +1是为了将换行字符也取出来
return ReadAsString(pos - ReadPosition() + 1);
}
std::string GetOneLineAndPop()
{
std::string str = GetOneLine();
MoveReadOffset(str.size());
return str;
}
// 清空缓冲区
void Clear()
{
_reader_idx = 0;
_writer_idx = 0;
}
};
2.日志宏的实现
#include 3.Socket模块实现
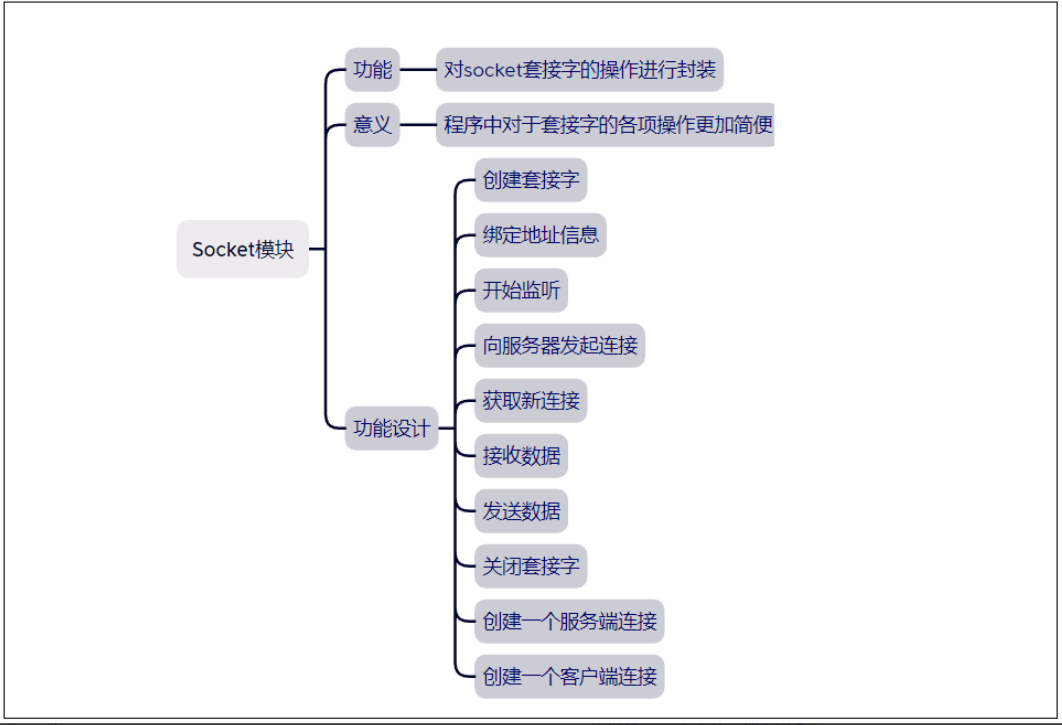
#define MAX_LISTEN 1024
class Socket
{
private:
int _sockfd;
public:
Socket() : _sockfd(-1) {}
Socket(int fd) : _sockfd(fd) {}
~Socket() { Close(); }
int Fd() { return _sockfd; }
public:
// 创建套接字
bool Create()
{
// int socket(int domain,int type,int protocol)
_sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
if (_sockfd < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "socket create failed");
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 绑定地址信息
bool Bind(const std::string &ip, const uint16_t &port)
{
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof local);
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(port);
local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
socklen_t len = sizeof(local);
// int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr,socklen_t addrlen);
int ret = bind(_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&local, len);
if (ret < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "socket bind failed");
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 开始监听
bool Listen(int backlog = MAX_LISTEN)
{
// int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);
int ret = listen(_sockfd, backlog);
if (ret < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "socket listen failed");
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 向服务器发起连接
bool Connect(const std::string &ip, const uint16_t &port)
{
struct sockaddr_in server;
memset(&server, 0, sizeof server);
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(port);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
socklen_t len = sizeof(server);
// int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr,socklen_t addrlen);
int ret = connect(_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server, len);
if (ret < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "socket connect failed");
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 获取新连接
int Accept()
{
// int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
int newfd = accept(_sockfd, nullptr, nullptr);
if (newfd < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "connect newfd failed");
return -1;
}
return newfd;
}
// 接收数据
ssize_t Recv(void *buf, size_t len, int flags = 0)
{
// ssize_t recv(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, int flags);
ssize_t ret = recv(_sockfd, buf, len, flags);
if (ret <= 0)
{
// EAGAIN表示当前socket的接收缓冲区中没有数据了,在非阻塞的情况下才会有这个错误
// EINTR 表示当前socket的阻塞等待,被信号打断了
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EINTR)
{
return 0;
}
LogMessage(FATAL, "recv message failed");
return -1;
}
// 返回实际接收到的长度
return ret;
}
// 非阻塞接收数据
ssize_t NonBlockRecv(void *buf, size_t len)
{
// MSG_DONTWAIT表示当接收为非阻塞
return Recv(buf, len, MSG_DONTWAIT);
}
// 发送数据
ssize_t Send(const void *buf, size_t len, int flags = 0)
{
// ssize_t send(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, int flags);
ssize_t ret = send(_sockfd, buf, len, flags);
if (ret < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR || errno == EAGAIN)
{
return 0;
}
LogMessage(FATAL, "send message failed");
return -1;
}
// 返回实际发送的长度
return ret;
}
// 非阻塞发送数据
ssize_t NonBlockSend(const void *buf, size_t len)
{
if (len == 0)
return 0;
// MSG_DONTWAIT表示当前发送为非阻塞
return Send(buf, len, MSG_DONTWAIT);
}
// 关闭套接字
void Close()
{
if (_sockfd != -1)
{
close(_sockfd);
_sockfd = -1;
}
}
// 创建一个服务端连接
bool CreateServer(const uint16_t &port, const std::string &ip = "0.0.0.0", bool block_flag = false)
{
// 1.创建套接字,2.设置非阻塞3.绑定地址,4.开始监听,5.启动地址重用
if (Create() == false)
return false;
if (block_flag)
NonBlock();
if (Bind(ip, port) == false)
return false;
if (Listen() == false)
return false;
ReuseAddress();
return true;
}
// 创建一个客户端连接
bool CreateClient(const uint16_t &port, const std::string &ip)
{
// 1.创建套接字,2,连接服务器
if (Create() == false)
return false;
if (Connect(ip, port) == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// 设置套接字选项 --开启地址端口重用
void ReuseAddress()
{
// int setsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname,const void *optval, socklen_t optlen);
int opt = 1;
setsockopt(_sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, (void *)&opt, sizeof opt);
opt = 1;
setsockopt(_sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEPORT, (void *)&opt, sizeof opt);
// int val = 1;
// setsockopt(_sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR | SO_REUSEPORT, (void*)&val, sizeof(val));
}
// 设置套接字属性--设置为非阻塞
void NonBlock()
{
// int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );
int flag = fcntl(_sockfd, F_GETFL, 0);
fcntl(_sockfd, F_SETFL, flag | O_NONBLOCK);
}
};
4.Channel模块实现

成员:因为后边使用epoll进行事件监控
EPOLLIN 可读
EPOLLOUT 可写
EPOLLRDHUP 连接断开
EPOLLPRI 优先数据
EPOLLERR 出错了
EPOLLHUP 挂断
class Channel
{
private:
uint32_t _events; // 当前需要监控的事件
uint32_t _revents; // 当前连接触发的事件
using EventCallback = std::function<void()>;
EventCallback _read_callback; // 可读事件被触发的回调函数
EventCallback _write_callback;// 可写事件被触发的回调函数
EventCallback _error_callback;// 错误事件被触发的回调函数
EventCallback _close_callback;// 连接断开事件被触发的回调函数
EventCallback _event_callback;// 任意事件被触发的回调函数
public:
Channel();
void SetReadCallback(const EventCallback& cb);
void SetWriteCallback(const EventCallback& cb);
void SetErrorCallback(const EventCallback& cb);
void SetCloseCallback(const EventCallback& cb);
void SetEventCallback(const EventCallback& cb);
bool ReadAble(); // 当前是否监控了可读
bool WriteAble(); // 当前是否监控了可写
void EnableRead(); // 启动可读事件
void EnableWrite(); // 启动可写事件
void DisableRead(); // 关闭读事件监控
void DisableWrite();//关闭写事件监控
void DisableAll();//关闭所有事件监控
void Remove(); // 移除监控
void Update();
void HandleEvent();//事件处理,一旦发生了事件,就调用这个函数,自己触发 什么事件如何处理自己决定
};
class Poller;
class EventLoop;
class Channel
{
private:
int _fd; // 文件描述符
EventLoop *_loop;
uint32_t _events; // 当前需要监控的事件
uint32_t _revents; // 当前连接触发的事件
using EventCallback = std::function<void()>;
EventCallback _read_callback; // 可读事件被触发的回调函数
EventCallback _write_callback; // 可写事件被触发的回调函数
EventCallback _error_callback; // 错误事件被触发的回调函数
EventCallback _close_callback; // 连接断开事件被触发的回调函数
EventCallback _event_callback; // 任意事件被触发的回调函数
public:
Channel(EventLoop *loop, int fd) : _fd(fd), _events(0), _revents(0), _loop(loop) {}
// 获取文件描述符
int Fd() { return _fd; }
// 获取想要监控的事件
uint32_t Events() { return _events; }
// 设置实际就绪事件
void SetRevents(const uint32_t &revents) { _revents = revents; }
// 设置回调函数
void SetReadCallback(const EventCallback &cb) { _read_callback = cb; }
void SetWriteCallback(const EventCallback &cb) { _write_callback = cb; }
void SetErrorCallback(const EventCallback &cb) { _error_callback = cb; }
void SetCloseCallback(const EventCallback &cb) { _close_callback = cb; }
void SetEventCallback(const EventCallback &cb) { _event_callback = cb; }
// 当前是否监控了可读
bool ReadAble() { return (_events & EPOLLIN); }
// 当前是否监控了可写
bool WriteAble() { return (_events & EPOLLOUT); }
// 启动可读事件
void EnableRead() { _events |= EPOLLIN; Update(); }
// 启动可写事件
void EnableWrite() { _events |= EPOLLOUT; Update(); }
// 关闭读事件监控
void DisableRead() { _events &= (~EPOLLIN); Update(); }
// 关闭写事件监控
void DisableWrite() { _events &= (~EPOLLOUT); Update(); }
// 关闭所有事件监控
void DisableAll() { _events = 0; Update(); }
// 移除监控
void Remove();
// 添加监控
void Update();
// 事件处理,一旦发生了事件,就调用这个函数,自己触发 什么事件如何处理自己决定
void HandleEvent()
{
// 可读事件就绪
if ((_revents & EPOLLIN) || (_revents & EPOLLRDHUP) || (_revents & EPOLLPRI))
{
if (_read_callback)
{
_read_callback();
}
if (_event_callback)
{
_event_callback();
}
}
// 可写事件就绪
if (_revents & EPOLLOUT)
{
if (_write_callback)
_write_callback();
if (_event_callback)
_event_callback();
}
// 错误事件 //一旦出错,就会释放连接,因此要放到前边调用任意回调
else if (_revents & EPOLLERR)
{
if (_event_callback)
_event_callback();
if (_error_callback)
_error_callback();
}
// 连接断开 //一旦出错,就会释放连接,因此要放到前边调用任意回调
else if (_revents & EPOLLHUP)
{
if (_event_callback)
_event_callback();
if (_close_callback)
_close_callback();
}
}
};
// 移除监控
void Channel::Remove() { return _loop->RemoveEvent(this); }
// 添加监控
void Channel::Update() { return _loop->UpdateEvent(this); }
3.描述符事件监控Poller类实现
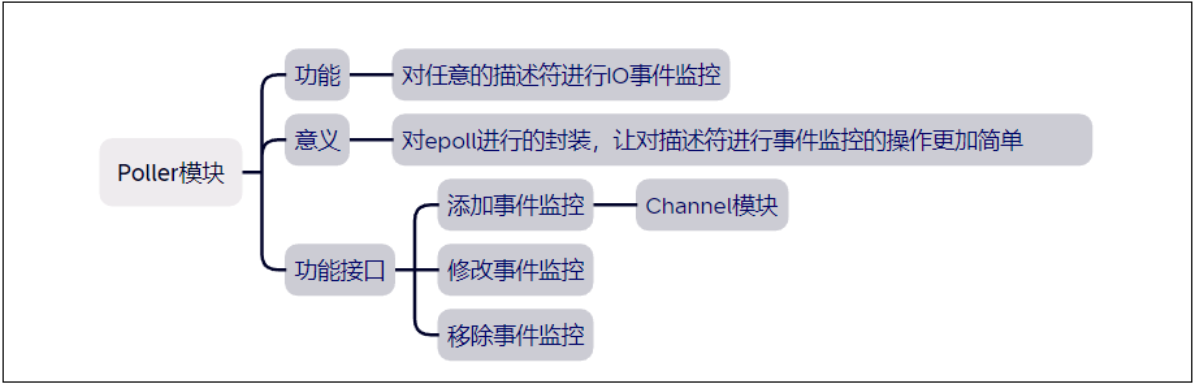
#define MAX_EPOLLEVENTS 1024
class Poller
{
private:
int _epfd;
struct epoll_event _evs[MAX_EPOLLEVENTS];
std::unordered_map<int,Channel*>;
private:
//1.判断要更新事件的描述符是否存在
//2.针对epoll直接操作(添加,修改,移除)
public:
//1.添加或更新描述符所监控的事件
//2.移除描述符的监控
//3.开始监控,获取就绪Channel
};
#define MAX_EPOLLEVENTS 1024
class Poller
{
private:
int _epfd;
struct epoll_event _evs[MAX_EPOLLEVENTS];
std::unordered_map<int,Channel*> _channels;
private:
// 对epoll的直接操作
void Update(Channel* channel,int op);
// 判断一个channel是否已经添加了事件监控
bool HashChannel(Channel* channel);
public:
Poller();
// 添加或修改监控事件
void UpdateEvent(Channel* channel);
// 移除监控
void RemoveEvent(Channel* channel);
// 开始监控,返回活跃连接
void Poll(std::vector<Channel*> active);
};
#define MAX_EPOLLEVENT 1024
class Poller
{
private:
int _epfd;
struct epoll_event _evs[MAX_EPOLLEVENT];
std::unordered_map<int, Channel *> _channels;
private:
// 对epoll的直接操作
void Update(Channel *channel, int op)
{
// int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = channel->Events();
ev.data.fd = channel->Fd();
int ret = epoll_ctl(_epfd, op, channel->Fd(), &ev);
if (ret < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "epollctl failed");
}
return;
}
// 判断一个channel是否已经添加了事件监控
bool HasChannel(Channel *Channel)
{
auto it = _channels.find(Channel->Fd());
return it != _channels.end();
// if(it == _channels.end()) return false;
// return true;
}
public:
Poller()
{
// int epoll_create(int size);
_epfd = epoll_create(MAX_EPOLLEVENT);
if (_epfd < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "epoll create failed");
abort();
}
}
// 添加或修改监控事件
void UpdateEvent(Channel *channel)
{
bool ret = HasChannel(channel);
// 不存在则添加
if (ret == false)
{
_channels.insert(std::make_pair(channel->Fd(), channel));
return Update(channel, EPOLL_CTL_ADD);
}
// 存在则修改
return Update(channel, EPOLL_CTL_MOD);
}
// 移除监控
void RemoveEvent(Channel *channel)
{
// bool ret = HasChannel(channel);
// if(ret != false)
// {
// _channels.erase(channel->Fd());
// return Update(channel,EPOLL_CTL_DEL);
// }
auto it = _channels.find(channel->Fd());
if (it != _channels.end())
{
_channels.erase(it);
return Update(channel, EPOLL_CTL_DEL);
}
}
// 开始监控,返回活跃连接
void Poll(std::vector<Channel *> *actives)
{
// int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events,int maxevents, int timeout);
int nfds = epoll_wait(_epfd, _evs, MAX_EPOLLEVENT, -1);
if (nfds < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
{
return;
}
LogMessage(FATAL, "epoll wait failed");
abort();
}
for (int i = 0; i < nfds; i++)
{
auto it = _channels.find(_evs[i].data.fd);
assert(it != _channels.end());
// 设置实际的就绪事件
it->second->SetRevents(_evs[i].events);
actives->push_back(it->second);
}
return;
}
};
4.EventLoop类的实现
#include #include 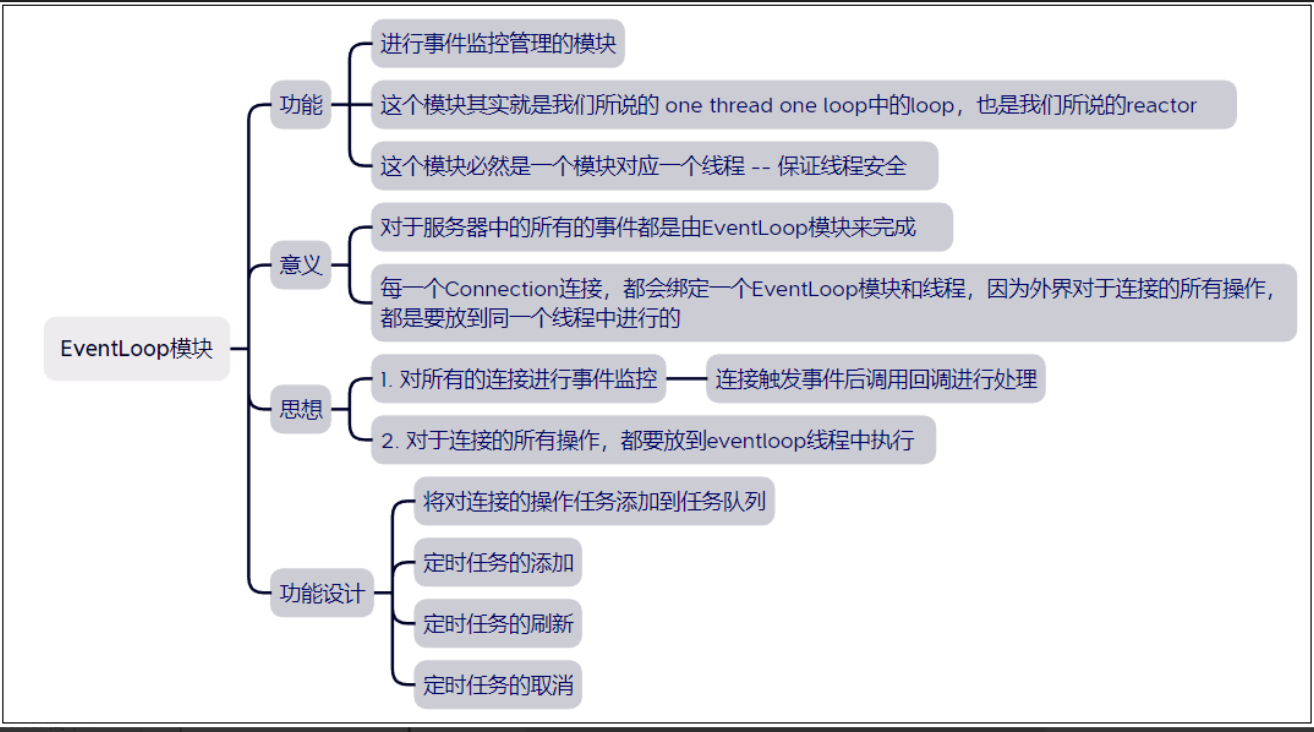

// 定时器任务的回调函数,即超时时执行的任务
using TaskFunc = std::function<void()>;
// 定时器对象销毁的回调函数
using ReleaseFunc = std::function<void()>;
// 定时器任务
class TimerTask
{
private:
uint64_t _id; // 定时器任务对象id
uint32_t _timeout; // 超时定时任务的超时时间
bool _canceled; // 超时任务:false表示没有被取消,true表示被取消了
TaskFunc _task_cb; // 定时器对象要执行的定时任务
ReleaseFunc _release; // 用于删除TimerWheel中保存的定时器对象信息
public:
TimerTask(const uint64_t &id, const uint32_t &delay, const TaskFunc &cb)
: _id(id), _timeout(delay), _task_cb(cb), _canceled(false) {}
~TimerTask()
{
if (_canceled == false)
_task_cb();
_release();
}
void Canceled() { _canceled = true; }
uint32_t DelayTime() { return _timeout; }
void SetRelease(const ReleaseFunc &cb) { _release = cb; }
};
// 管理定时器任务的shared_ptr
using PtrTask = std::shared_ptr<TimerTask>;
// 管理定时器任务的weak_ptr
using WeakTask = std::weak_ptr<TimerTask>;
class EventLoop;
// 时间轮
class TimerWheel
{
private:
int _tick; // 当前的秒针,走到哪里释放哪里,就相当于执行哪里的任务
int _capacity; // 表盘的最大数量,即最大延迟时间
std::vector<std::vector<PtrTask>> _wheel;
std::unordered_map<uint64_t, WeakTask> _timers;
EventLoop *_loop;
int _timerfd; // 定时器描述符--可读事件回调就是读取定时器,并执行定时任务
std::unique_ptr<Channel> _timer_channel;
private:
void RemoveTimer(const uint64_t &id)
{
auto it = _timers.find(id);
if (it != _timers.end())
{
_timers.erase(it);
}
}
// 创建定时器描述符
static int CreateTimerfd()
{
// 创建一个定时器
int timerfd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0);
if (timerfd < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "create timerfd failed");
abort();
}
// 设置超时时间
struct itimerspec ims;
// 第一次超时时间为1s后
ims.it_value.tv_sec = 1;
ims.it_value.tv_nsec = 0;
// 第一次超时后,每次超时的间隔时
ims.it_interval.tv_sec = 1;
ims.it_interval.tv_nsec = 0;
// 启动定时器
int n = timerfd_settime(timerfd, 0, &ims, nullptr);
if (n < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "timerfd settime failed");
abort();
}
return timerfd;
}
// 读取定时器描述符的数据
int ReadTimerfd()
{
uint64_t times;
ssize_t ret = read(_timerfd, ×, 8);
if (ret < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "read timerfd failed");
abort();
}
return times;
}
// 这个函数应该每秒钟被执行一次,相当于秒针向后走了一步
void RunTimerTask()
{
_tick = (_tick + 1) % _capacity;
// 清空指定位置的数组,就会把数组中保存的所有管理定时器对象的shared_ptr释放掉
_wheel[_tick].clear();
}
// 定时器读事件的回调函数
void OnTime()
{
// 根据实际超时的次数,执行对应的超时任务
int times = ReadTimerfd();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++)
{
RunTimerTask();
}
}
// 添加定时任务
void TimerAddInLoop(const uint64_t &id, const uint32_t &delay, const TaskFunc &cb)
{
PtrTask ptr(new TimerTask(id, delay, cb));
ptr->SetRelease(std::bind(&TimerWheel::RemoveTimer, this, id));
int pos = (_tick + delay) % _capacity;
// 将shared_ptr管理的对象加入到时间轮中
_wheel[pos].push_back(ptr);
// 将shared_ptr管理的对象的weak_ptr加入到哈希表中
_timers[id] = WeakTask(ptr);
}
// 刷新/延迟定时时间
void TimerRefreshInLoop(const uint64_t &id)
{
// 通过保存的定时器的weak_ptr构造一个shared_ptr出来,添加到轮子中
auto it = _timers.find(id);
// 没找着定时任务,没法刷新,没法延迟
if (it == _timers.end())
{
return;
}
// lock获取weak_ptr管理的对象对应的shared_ptr
PtrTask ptr = it->second.lock();
int delay = ptr->DelayTime();
int pos = (_tick + delay) % _capacity;
_wheel[pos].push_back(ptr);
}
// 取消定时任务
void TimerCancelInLoop(const uint64_t &id)
{
auto it = _timers.find(id);
// 没有找到定时任务就没法刷新和延迟,直接退出
if (it == _timers.end())
return;
PtrTask ptr = it->second.lock();
if (ptr)
ptr->Canceled();
}
public:
TimerWheel(EventLoop *loop)
: _tick(0), _capacity(60), _wheel(_capacity),
_loop(loop), _timerfd(CreateTimerfd()),
_timer_channel(new Channel(_loop, _timerfd))
{
_timer_channel->SetReadCallback(std::bind(&TimerWheel::OnTime, this));
_timer_channel->EnableRead(); // 启动读事件
}
// 定时器有个成员_timers成员,定时器信息的操作有可能在多个线程中进行,因此要考虑线程安全
// 如果不想加锁,那就把对定时器的所有操作,都放到一个线程中执行
// 添加定时任务
void TimerAdd(const uint64_t &id, const uint32_t &delay, const TaskFunc &cb);
// 刷新/延迟定时时间
void TimerRefresh(const uint64_t &id);
// 取消定时任务
void TimerCancel(const uint64_t &id);
// 存在线程安全问题,不能被外界使用者调用,只能在模块内,在对应的EventLoop线程内调用
bool HasTimer(const uint64_t &id)
{
auto it = _timers.find(id);
// 没有找到定时任务就没法刷新和延迟,直接退出
if (it == _timers.end())
return false;
return true;
}
};
// 添加定时任务
void TimerWheel::TimerAdd(const uint64_t &id, const uint32_t &delay, const TaskFunc &cb)
{
return _loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&TimerWheel::TimerAddInLoop, this, id, delay, cb));
}
// 刷新/延迟定时时间
void TimerWheel::TimerRefresh(const uint64_t &id)
{
return _loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&TimerWheel::TimerRefreshInLoop, this, id));
}
// 取消定时任务
void TimerWheel::TimerCancel(const uint64_t &id)
{
return _loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&TimerWheel::TimerCancelInLoop, this, id));
}
using Functor = std::function<void()>;
class EventLoop
{
private:
std::thread::id _thread_id; // 线程ID
int _event_fd; // eventfd唤醒IO事件监控有可能导致的阻塞
std::unique_ptr<Channel> _event_channel;
Poller _poller; // 进行描述符的事件监控
std::vector<Functor> _tasks; // 任务池
std::mutex _mutex; // 实现任务池操作的线程安全
TimerWheel _timer_wheel; // 定时器模块
private:
// 执行任务池中的所有任务
void RunAllTask()
{
std::vector<Functor> functor;
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(_mutex);
_tasks.swap(functor);
}
for (auto &func : functor)
{
func();
}
return;
}
// 创建一个eventfd对象,实现事件通知
static int CreateEventFd()
{
// int eventfd(unsigned int initval, int flags);
// EFD_CLOEXEC--禁止进程复制
// EFD_NONBLCK--启动非阻塞属性
int efd = eventfd(0, EFD_CLOEXEC | EFD_NONBLOCK);
if (efd < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "eventfd create failed");
abort();
}
return efd;
}
// 读取eventfd中的数据,来完成清0-线程接收通知
void ReadEventFd()
{
uint64_t res = 0;
int ret = read(_event_fd, &res, sizeof(res));
if (ret <= 0)
{
// EINTR----被信号打断 EAGAIN -- 表示无数据可读
if (errno == EINTR || errno == EAGAIN)
{
return;
}
LogMessage(FATAL, "read eventfd failed");
abort();
}
return;
}
// 向eventfd写入数据,实现线程的通知
void WeakUpEventFd()
{
uint64_t val = 1;
int ret = write(_event_fd, &val, sizeof(val));
if (ret <= 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
{
return;
}
LogMessage(FATAL, "write eventfd failed");
abort();
}
return;
}
public:
EventLoop() : _thread_id(std::this_thread::get_id()),
_event_fd(CreateEventFd()),
_event_channel(new Channel(this, _event_fd)),
_timer_wheel(this)
{
// 给eventfd 添加可读事件回调函数,读取eventfd事件通知次数
_event_channel->SetReadCallback(std::bind(&EventLoop::ReadEventFd, this));
// 启动eventfd的读事件监控
_event_channel->EnableRead();
}
// 三步走---事件监控--》就绪事件处理--》执行任务
void Start()
{
for (;;)
{
// 1.事件监控
std::vector<Channel *> actives;
_poller.Poll(&actives);
// 2.就绪事件处理
for (auto &channel : actives)
{
channel->HandleEvent();
}
// 3.执行任务
RunAllTask();
}
}
// 用于判断当前线程是否是EventLoop对应的线程
bool IsInLoop()
{
return _thread_id == std::this_thread::get_id();
}
void AssertInLoop()
{
assert(_thread_id == std::this_thread::get_id());
}
// 判断将要执行的任务是否处于当前线程中
void RunInLoop(const Functor &cb)
{
if (IsInLoop())
{
return cb();
}
return QueueInLoop(cb);
}
// 将操作压入任务池
void QueueInLoop(const Functor &cb)
{
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(_mutex);
_tasks.push_back(cb);
}
// 唤醒有可能因为没有事件就绪,而导致的epoll阻塞
// 其实就是给eventfd写入一个数据,eventfd就会触发可读事件
WeakUpEventFd();
}
// 添加/修改描述符的事件监控
void UpdateEvent(Channel *channel)
{
return _poller.UpdateEvent(channel);
}
// 移除描述符的事件监控
void RemoveEvent(Channel *channel)
{
return _poller.RemoveEvent(channel);
}
// 添加定时任务
void TimerAdd(const uint64_t &id, const uint32_t &delay, const TaskFunc &cb)
{
return _timer_wheel.TimerAdd(id, delay, cb);
}
// 刷新定时任务
void TimerRefresh(const uint64_t &id)
{
return _timer_wheel.TimerRefresh(id);
}
// 取消定时任务
void TimerCancel(const uint64_t &id)
{
return _timer_wheel.TimerCancel(id);
}
bool HasTimer(const uint64_t &id)
{
return _timer_wheel.HasTimer(id);
}
};
4.通信连接管理Connection类实现
1.套接字的管理,能够进行套接字的操作
1.发送数据—给用户提供的发送数据接口,并不是真正的发送接口,而只是把数据放到发送缓冲区,然后启动写事件监控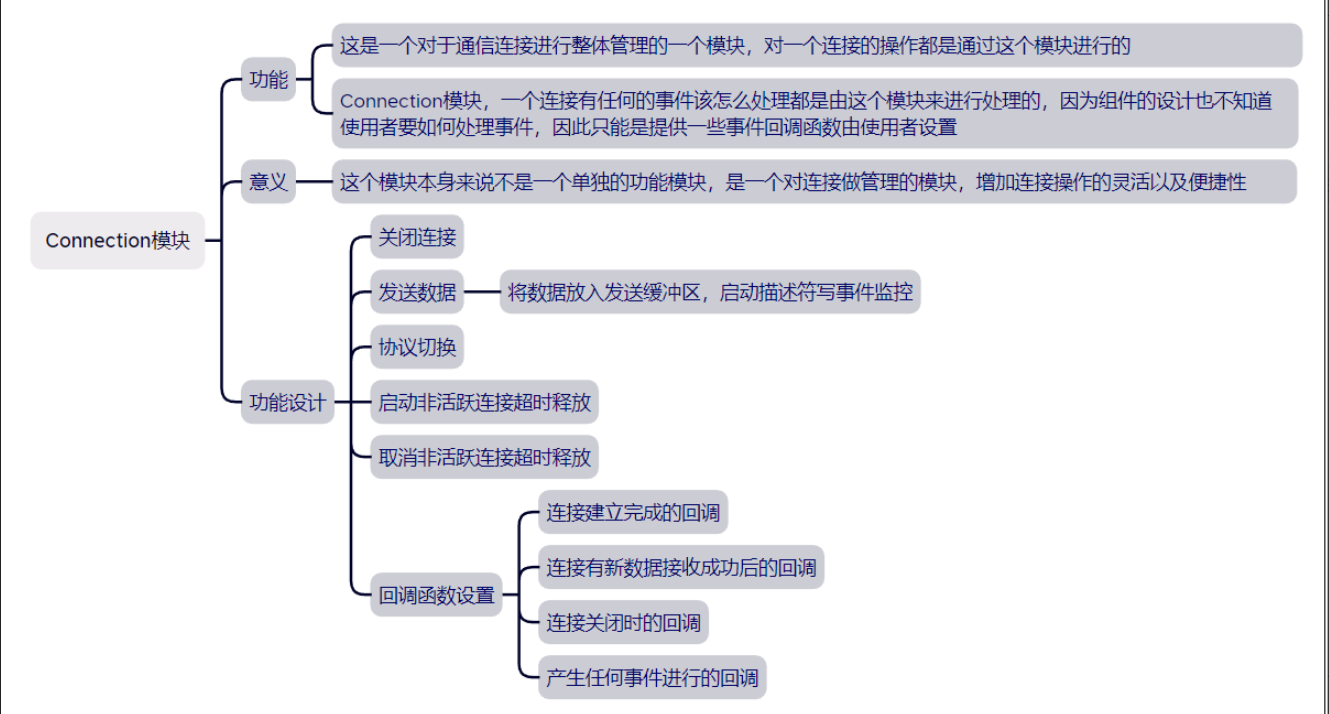
class Connection;
// DISCONNECTED -- 连接关闭状态 CONNECTING -- 连接建立成功
// CONNECTED -- 连接建立完成,各种设置已完成,可以通信的状态
// DISCONNECTING -- 待关闭的状态
typedef enum
{
DISCONNECTED,
CONNECTING,
CONNECTED,
DISCONNECTING
} ConnStatu;
using PtrConnection = std::shared_ptr<Connection>;
class Connection
{
private:
uint64_t _conn_id; // 连接的唯一ID
// uint64_t _timer_id; // 定时器ID,必须是唯一的,这块为了简化操作使用conn_id作为定时器ID
int _sockfd; // 连接关联的文件描述符
bool _enable_inactive_release; // 连接是否启动非活跃销毁的判断标志,默认为false
ConnStatu _statu; // 连接的状态
Socket _socket; // 套接字操作管理
Channel _channel; // 连接的事件管理
Buffer _in_buffer; // 输入缓冲区--存放从socket中读到的数据
Buffer _out_buffer; // 输出缓冲区--存放要发送给对端的数据
Any _context; // 请求的接收处理的上下文
/*这四个回调函数,是让服务器模块来设置的(其实服务器模块的处理回调也是组件使用者设置的)*/
/*换句话说,这几个回调都是组件使用者使用的*/
using ConnectedCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using MessageCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &, Buffer *)>;
using ClosedCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using AnyEventCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
ConnectedCallback _connected_callback;
MessageCallback _message_callback;
ClosedCallback _closed_callback;
AnyEventCallback _event_callback;
ClosedCallback _server_closed_callback;
private:
// 五个Channel的事件回调函数
void HandleRead();//描述符可读事件触发后的回调函数
void HandleWrite();//描述符可写事件触发后的回调函数
void HandleClose();//描述符挂断事件触发后的回调函数
void HandleError();//描述符错误事件触发后的回调函数
void HandleEvent();//描述符任意事件触发后的回调函数
void EstableishdInLoop();//连接获取之后,所处的状态下要进行的各种设置(给Channel设置事件回调,启动读监控)
void ReleaseInLoop();
void SendInLoop(const char *data, int len);
void ShutDownInLoop();
void EnableInactiveReleaseInLoop(int sec);
void CancelInactiveReleaseInLoop();
void UpgrateInLoop(const Any &context,
const ConnectedCallback &conn,
const MessageCallback &msg,
const ClosedCallback &closed,
const AnyEventCallback &event);
public:
Connection(EventLoop *loop, const uint64_t &conn_id, int sockfd);
~Connection();
int Fd(); // 获取管理的文件描述符
int Id(); // 获取连接ID
bool Connected(); // 是否处于CONNECTED状态
void SetContext(const Any &context); // 设置上下文
Any *GetContext(); // 获取上下文,返回的是指针
void SetConnextedCallback(const ConnectedCallback &cb);
void SetMessageCallback(const MessageCallback &cb);
void SetClosedCallback(const ClosedCallback &cb);
void SetAnyEventedCallback(const AnyEventCallback &cb);
// 连接建立就绪后,进行channel回调设置,启动读监控,调用_connected_callback
void Established();
// 发送数据,将数据放到发送缓冲区,启动写事件监控
void Send(const char *data, size_t len);
// 提供给组件使用者的关闭接口 --并不实际关闭,需要判断有没有数据待处理
void Shutdown();
// 启动非活跃销毁,并定义多长时间无通信就是非活跃,添加定时任务
void EnableInactiveRelease(int sec);
// 取消非活跃销毁
void CancleInactiveRelease(int sec);
// 切换协议--重置上下文以及阶段性处理函数
void Update(const Any &context, const ConnectedCallback &conn, const MessageCallback &msg,
const ClosedCallback &closed, const AnyEventCallback &event);
};
class Connection;
// DISCONNECTED -- 连接关闭状态 CONNECTING -- 连接建立成功
// CONNECTED -- 连接建立完成,各种设置已完成,可以通信的状态
// DISCONNECTING -- 待关闭的状态
typedef enum
{
DISCONNECTED,
CONNECTING,
CONNECTED,
DISCONNECTING
} ConnStatu;
using PtrConnection = std::shared_ptr<Connection>;
class Connection : public std::enable_shared_from_this<Connection>
{
private:
uint64_t _conn_id; // 连接的唯一ID
// uint64_t _timer_id; // 定时器ID,必须是唯一的,这块为了简化操作使用conn_id作为定时器ID
int _sockfd; // 连接关联的文件描述符
bool _enable_inactive_release; // 连接是否启动非活跃销毁的判断标志,默认为false
EventLoop *_loop; // 连接所关联的一个EventLoop
ConnStatu _statu; // 连接的状态
Socket _socket; // 套接字操作管理
Channel _channel; // 连接的事件管理
Buffer _in_buffer; // 输入缓冲区--存放从socket中读到的数据
Buffer _out_buffer; // 输出缓冲区--存放要发送给对端的数据
Any _context; // 请求的接收处理的上下文
/*这四个回调函数,是让服务器模块来设置的(其实服务器模块的处理回调也是组件使用者设置的)*/
/*换句话说,这几个回调都是组件使用者使用的*/
using ConnectedCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using MessageCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &, Buffer *)>;
using ClosedCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using AnyEventCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
ConnectedCallback _connected_callback;
MessageCallback _message_callback;
ClosedCallback _closed_callback;
AnyEventCallback _event_callback;
/*组件内的连接关闭回调--组件内设置的,因为服务器组件内会把所有的连接管理起来,一旦某个连接要关闭*/
/*就应该从管理的地方移除掉自己的信息*/
ClosedCallback _server_closed_callback;
private:
// 五个Channel的事件回调函数
// 描述符可读事件触发后的回调函数
void HandleRead()
{
// 1.接收socket的数据,放到缓冲区
char buffer[65536];
ssize_t ret = _socket.NonBlockRecv(buffer, 65535);
if (ret < 0)
{
// 出错了,不能直接关闭连接
return ShutDownInLoop();
}
else if (ret == 0)
{
// 这里等于0表示的是没有读到数据,而并不是连接断开了,连接断开返回的是-1
return;
}
// 将数据放入输入缓冲区
_in_buffer.WriteAndPush(buffer, ret);
// 2.调用message_callback进行业务处理
if (_in_buffer.ReadAbleSize() > 0)
{
// shared_from_this从当前对象自身获取自身的shared_ptr管理对象
// 需要当前类继承enable_shared_from_this5.监听描述符管理Acceptor类实现

class Acceptor
{
private:
Socket _socket; // 同于创建监听套接字
EventLoop *_loop; // 对于监听套接字进行事件监控
Channel _channel; // 对于监控套接字进行事件管理
using AcceptCallback = std::function<void(int)>;
AcceptCallback _accept_callback;
private:
int CreateServer(const uint16_t &port)
{
bool ret = _socket.CreateServer(port);
assert(ret == true);
return _socket.Fd();
}
// 监听套接字的读事件回调处理函数,获取新连接,调用_accept_callback函数进行新连接处理
void HandleRead()
{
int newfd = _socket.Accept();
if (newfd < 0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "accept new fd failed");
return;
}
if (_accept_callback)
_accept_callback(newfd);
}
public:
/*不能将启动读事件监控,放到构造函数中,必须在设置回调函数后,再去启动*/
/*否则有可能造成启动监控后,立即有事件,处理的时候,回调函数还没设置:新连接得不到处理,且资源泄漏*/
Acceptor(EventLoop *loop, const uint16_t &port)
: _socket(CreateServer(port)), _loop(loop),
_channel(_loop, _socket.Fd())
{
_channel.SetReadCallback(std::bind(&Acceptor::HandleRead, this));
}
void SetAcceptCallback(const AcceptCallback &cb)
{
_accept_callback = cb;
}
void Listen()
{
_channel.EnableRead();
}
};
6.LoopThread类的实现
class LoopThread
{
private:
/*用于实现_loop获取的同步关系,避免线程创建了,但是_loop还没有实例化之前去获取_loop*/
std::mutex _mutex; // 互斥锁
std::condition_variable _cond; // 条件变量
EventLoop *_loop; // EventLoop指针变量,这个对象需要在线程内实例化
std::thread _thread; // EventLoop对应的线程
private:
/*实例化 EventLoop 对象,唤醒_cond上有可能阻塞的线程,并且开始运行EventLoop模块的功能*/
void ThreadEntry()
{
EventLoop loop;
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(_mutex);
_loop = &loop;
_cond.notify_all();
}
loop.Start();
}
public:
/*创建线程,设定线程入口函数*/
LoopThread() : _thread(std::thread(&LoopThread::ThreadEntry, this)), _loop(nullptr) {}
/*返回当前线程关联的EventLoop对象指针*/
EventLoop *GetEventLoop()
{
EventLoop *loop = nullptr;
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(_mutex); // 加锁
_cond.wait(lock, [&]()
{ return _loop != nullptr; }); //_loop为nullptr就一直阻塞
loop = _loop;
}
return loop;
}
};
8.LoopThreadPool类的实现
class LoopThreadPool
{
private:
int _thread_count;//从属线程的数量
int _next_loop_id;
EventLoop* _baseloop;//主EventLoop,运行在主线程,从属线程数量为0,则所有的操作都在baseloop中运行
std::vector<LoopThread*> _threads;//保存所有的LoopThread对象
std::vector<EventLoop*> _loops;//从属线程数量大于0则从_loops中进行线程EventLoop分配
public:
LoopThreadPool();
void SetThreadCount(int count);//设置线程数量
void Create();//创建所有的从属线程
EventLoop* GetNextLoop();
};
class LoopThreadPool
{
private:
int _thread_count; // 从属线程的数量
int _next_idx; // RR轮转的下标
EventLoop *_base_loop; // 主EventLoop,运行在主线程,从属线程数量为0,则所有的操作都在baseloop中运行
std::vector<LoopThread *> _threads; // 保存所有的LoopThread对象
std::vector<EventLoop *> _loops; // 从属线程数量大于0则从_loops中进行线程EventLoop分配
public:
LoopThreadPool(EventLoop *baesloop)
: _thread_count(0), _next_idx(0), _base_loop(baesloop) {}
void SetThreadCount(const int &count) { _thread_count = count; }
void Create()
{
if (_thread_count > 0)
{
_threads.resize(_thread_count);
_loops.resize(_thread_count);
for (int i = 0; i < _thread_count; i++)
{
_threads[i] = new LoopThread();
_loops[i] = _threads[i]->GetEventLoop();
}
}
}
EventLoop *GetNextLoop()
{
if (_thread_count == 0)
{
return _base_loop;
}
_next_idx = (_next_idx + 1) % _thread_count;
return _loops[_next_idx];
}
};
9.服务器TcpServer类实现

class TcpServer
{
private:
uint64_t _next_id; // 这是一个自动增长的连接ID
uint16_t _port;
int _timeout; // 这是非活跃连接的统计时间---多长时间无通信就是非活跃连接
bool _enable_inactive_release; // 是否启动了非活跃连接超时销毁的判断标志
EventLoop _baseloop; // 这是主线程的EventLoop对象,负责监听事件的处理
Acceptor _acceptor; // 这是监听套接字的管理对象
LoopThreadPool _pool; // 这是从属EventLoop线程池
std::unordered_map<uint64_t, PtrConnection> _conns; // 保存管理所有连接对应的shared_ptr对象
using ConnectedCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using MessageCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &, Buffer *)>;
using ClosedCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using AnyEventCallback = std::function<void(const PtrConnection &)>;
using Functor = std::function<void()>;
ConnectedCallback _connected_callback;
MessageCallback _message_callback;
ClosedCallback _closed_callback;
AnyEventCallback _event_callback;
private:
// 添加定时任务
void RunAfterInLoop(const Functor &task, int delay)
{
_next_id++;
_baseloop.TimerAdd(_next_id, delay, task);
}
// 为新连接构造一个Connection进行管理
void NewConnection(int fd)
{
_next_id++;
PtrConnection conn(new Connection(_pool.GetNextLoop(), _next_id, fd));
conn->SetConnectedCallback(_connected_callback);
conn->SetClosedCallback(_closed_callback);
conn->SetMessageCallback(_message_callback);
conn->SetAnyEventedCallback(_event_callback);
conn->SetSrvClosedCallback(std::bind(&TcpServer::RemoveConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));
// 启动非活跃连接释放
if (_enable_inactive_release)
conn->EnableInactiveRelease(_timeout);
conn->Established();
_conns.insert(std::make_pair(_next_id, conn));
}
void RemoveConnectionInLoop(const PtrConnection &conn)
{
int id = conn->Id();
auto it = _conns.find(id);
if (it != _conns.end())
{
_conns.erase(id);
}
}
// 从管理Connection的_conns中移除连接信息
void RemoveConnection(const PtrConnection &conn)
{
_baseloop.RunInLoop(std::bind(&TcpServer::RemoveConnectionInLoop, this, conn));
}
public:
TcpServer(const uint16_t &port)
: _next_id(0),
_port(port),
_enable_inactive_release(false),
_acceptor(&_baseloop, port),
_pool(&_baseloop)
{
// 设置监听套接字读事件的回调函数
_acceptor.SetAcceptCallback(std::bind(&TcpServer::NewConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));
// 将监听套接字挂到baseloop上
_acceptor.Listen();
}
// 设置线程数量
void SetThreadCount(int count) { _pool.SetThreadCount(count); }
void SetConnectedCallback(const ConnectedCallback &cb) { _connected_callback = cb; }
void SetMessageCallback(const MessageCallback &cb) { _message_callback = cb; }
void SetClosedCallback(const ClosedCallback &cb) { _closed_callback = cb; }
void SetAnyEventCallback(const AnyEventCallback &cb) { _event_callback = cb; }
// 启动非活跃连接销毁
void EnableInactiveRelease(int timeout)
{
_enable_inactive_release = true;
_timeout = timeout;
}
// 用于添加一个定时任务
void RunAfter(const Functor &task, int delay)
{
_baseloop.RunInLoop(std::bind(&TcpServer::RunAfterInLoop, this, task, delay));
}
// 启动服务器
void Start()
{
// 线程池的创建
_pool.Create();
// 事件监控--》就绪事件处理--》执行任务
_baseloop.Start();
}
};
10.基于TcpServer实现回显服务器
#include "../server.hpp"
class EchoServer
{
private:
TcpServer _server;
private:
void OnConnected(const PtrConnection &conn)
{
DLOG("NEW CONNECTION: %p", conn.get());
}
void OnClosed(const PtrConnection &conn)
{
DLOG("CLOSE CONNECTION: %p", conn.get());
}
void OnMessage(const PtrConnection &conn, Buffer *buf)
{
conn->Send(buf->ReadPosition(), buf->ReadAbleSize());
buf->MoveReadOffset(buf->ReadAbleSize());
conn->Shutdown();
}
public:
EchoServer(const uint16_t &port) : _server(port)
{
_server.SetThreadCount(2);
_server.EnableInactiveRelease(10);
_server.SetConnectedCallback(std::bind(&EchoServer::OnConnected, this, std::placeholders::_1));
_server.SetClosedCallback(std::bind(&EchoServer::OnClosed, this, std::placeholders::_1));
_server.SetMessageCallback(std::bind(&EchoServer::OnMessage, this, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2));
}
void Start()
{
_server.Start();
}
};
#include "../source/server.hpp"
int main()
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
// 向服务器发送数据
std::string str = "hello server";
clientsock.Send(str.c_str(), str.size());
// 接收服务器响应
char buffer[1024];
ssize_t n = clientsock.Recv(buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
buffer[n] = 0;
LogMessage(NORMAL,"[echo]# %s", buffer);
sleep(1);
}
while (true)
sleep(1);
clientsock.Close();
return 0;
}
#include "echo.hpp"
int main()
{
EchoServer server(8080);
server.Start();
return 0;
}
七、HTTP协议模块
1.Util工具类实现

std::unordered_map<int, std::string> _statu_msg = {
{100, "Continue"},
{101, "Switching Protocol"},
{102, "Processing"},
{103, "Early Hints"},
{200, "OK"},
{201, "Created"},
{202, "Accepted"},
{203, "Non-Authoritative Information"},
{204, "No Content"},
{205, "Reset Content"},
{206, "Partial Content"},
{207, "Multi-Status"},
{208, "Already Reported"},
{226, "IM Used"},
{300, "Multiple Choice"},
{301, "Moved Permanently"},
{302, "Found"},
{303, "See Other"},
{304, "Not Modified"},
{305, "Use Proxy"},
{306, "unused"},
{307, "Temporary Redirect"},
{308, "Permanent Redirect"},
{400, "Bad Request"},
{401, "Unauthorized"},
{402, "Payment Required"},
{403, "Forbidden"},
{404, "Not Found"},
{405, "Method Not Allowed"},
{406, "Not Acceptable"},
{407, "Proxy Authentication Required"},
{408, "Request Timeout"},
{409, "Conflict"},
{410, "Gone"},
{411, "Length Required"},
{412, "Precondition Failed"},
{413, "Payload Too Large"},
{414, "URI Too Long"},
{415, "Unsupported Media Type"},
{416, "Range Not Satisfiable"},
{417, "Expectation Failed"},
{418, "I'm a teapot"},
{421, "Misdirected Request"},
{422, "Unprocessable Entity"},
{423, "Locked"},
{424, "Failed Dependency"},
{425, "Too Early"},
{426, "Upgrade Required"},
{428, "Precondition Required"},
{429, "Too Many Requests"},
{431, "Request Header Fields Too Large"},
{451, "Unavailable For Legal Reasons"},
{501, "Not Implemented"},
{502, "Bad Gateway"},
{503, "Service Unavailable"},
{504, "Gateway Timeout"},
{505, "HTTP Version Not Supported"},
{506, "Variant Also Negotiates"},
{507, "Insufficient Storage"},
{508, "Loop Detected"},
{510, "Not Extended"},
{511, "Network Authentication Required"}};
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _mime_msg = {
{".aac", "audio/aac"},
{".abw", "application/x-abiword"},
{".arc", "application/x-freearc"},
{".avi", "video/x-msvideo"},
{".azw", "application/vnd.amazon.ebook"},
{".bin", "application/octet-stream"},
{".bmp", "image/bmp"},
{".bz", "application/x-bzip"},
{".bz2", "application/x-bzip2"},
{".csh", "application/x-csh"},
{".css", "text/css"},
{".csv", "text/csv"},
{".doc", "application/msword"},
{".docx", "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document"},
{".eot", "application/vnd.ms-fontobject"},
{".epub", "application/epub+zip"},
{".gif", "image/gif"},
{".htm", "text/html"},
{".html", "text/html"},
{".ico", "image/vnd.microsoft.icon"},
{".ics", "text/calendar"},
{".jar", "application/java-archive"},
{".jpeg", "image/jpeg"},
{".jpg", "image/jpeg"},
{".js", "text/javascript"},
{".json", "application/json"},
{".jsonld", "application/ld+json"},
{".mid", "audio/midi"},
{".midi", "audio/x-midi"},
{".mjs", "text/javascript"},
{".mp3", "audio/mpeg"},
{".mpeg", "video/mpeg"},
{".mpkg", "application/vnd.apple.installer+xml"},
{".odp", "application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.presentation"},
{".ods", "application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.spreadsheet"},
{".odt", "application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.text"},
{".oga", "audio/ogg"},
{".ogv", "video/ogg"},
{".ogx", "application/ogg"},
{".otf", "font/otf"},
{".png", "image/png"},
{".pdf", "application/pdf"},
{".ppt", "application/vnd.ms-powerpoint"},
{".pptx", "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation"},
{".rar", "application/x-rar-compressed"},
{".rtf", "application/rtf"},
{".sh", "application/x-sh"},
{".svg", "image/svg+xml"},
{".swf", "application/x-shockwave-flash"},
{".tar", "application/x-tar"},
{".tif", "image/tiff"},
{".tiff", "image/tiff"},
{".ttf", "font/ttf"},
{".txt", "text/plain"},
{".vsd", "application/vnd.visio"},
{".wav", "audio/wav"},
{".weba", "audio/webm"},
{".webm", "video/webm"},
{".webp", "image/webp"},
{".woff", "font/woff"},
{".woff2", "font/woff2"},
{".xhtml", "application/xhtml+xml"},
{".xls", "application/vnd.ms-excel"},
{".xlsx", "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet"},
{".xml", "application/xml"},
{".xul", "application/vnd.mozilla.xul+xml"},
{".zip", "application/zip"},
{".3gp", "video/3gpp"},
{".3g2", "video/3gpp2"},
{".7z", "application/x-7z-compressed"}};
class Util
{
public:
// 字符串分割函数,将src字符串按照sep字符进行分割,得到的各个字串放到arry中,最终返回字串的数量
static size_t Split(const std::string &src, const std::string &sep, std::vector<std::string> *array)
{
// abc,,,de,f,
size_t offset = 0;
// 有10个字符,offset是查找的起始位置,范围应该是0~9,offset==10就代表已经越界了
while (offset < src.size())
{
// 在src字符串偏移量offset处,开始向后查找sep字符/字串,返回查找到的位置
size_t pos = src.find(sep, offset);
// 没有找到特定的字符将剩余的部分当作一个字串,放入arry中
if (pos == std::string::npos)
{
// if (pos == src.size())
// break;
array->push_back(src.substr(offset));
return array->size();
}
// 连续分割字符则跳过字符
if (offset == pos)
{
offset = pos + sep.size();
continue;
}
array->push_back(src.substr(offset, pos - offset));
offset = pos + sep.size();
}
return array->size();
}
// 读取文件的所有内容,将读取的内容放到一个Buffer中
static bool ReadFile(const std::string &filename, std::string *buf)
{
std::ifstream ifs(filename, std::ios::binary);
if (ifs.is_open() == false)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "%s open failed", filename.c_str());
return false;
}
size_t fsize = 0;
// 跳转读写位置到末尾
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.end);
// 获取当前读写位置相对于起始位置的偏移量,从末尾偏移刚好就是文件大小
fsize = ifs.tellg();
// 跳转到起始位置
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.beg);
// 开辟文件大小的空间
buf->resize(fsize);
ifs.read(&(*buf)[0], fsize);
if (ifs.good() == false)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "%s read failed", filename.c_str());
ifs.close();
return false;
}
ifs.close();
return true;
}
// 向文件写入数据
static bool WriteFile(const std::string &filename, const std::string &buf)
{
std::ofstream ofs(filename, std::ios::binary | std::ios::trunc);
if (ofs.is_open() == false)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "%s open failed", filename.c_str());
return false;
}
ofs.write(buf.c_str(), buf.size());
if (ofs.good() == false)
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "%s write failed", filename.c_str());
ofs.close();
return false;
}
ofs.close();
return true;
}
// URL编码,避免URL中资源路径与查询字符串中的特殊字符与HTTP请求中特殊字符产生歧义
// 编码格式:将特殊字符的ascii值,转换为两个16进制字符,前缀% C++ -> C%2B%2B
// 不编码的特殊字符: RFC3986文档规定 . - _ ~ 字母,数字属于绝对不编码字符
// RFC3986文档规定,编码格式 %HH
// W3C标准中规定,查询字符串中的空格,需要编码为+, 解码则是+转空格
static std::string UrlEncode(const std::string &url, bool convert_space_to_plus = false)
{
std::string res;
for (auto ch : url)
{
// isalnum 是 C++ 中用于判断字符是否为字母或数字的函数
if (ch == '.' || ch == '-' || ch == '_' || ch == '~' || isalnum(ch))
{
res += ch;
continue;
}
if (ch == ' ' && convert_space_to_plus)
{
res += '+';
continue;
}
// 剩下的字符都是需要编码成为 %HH 格式
char tmp[4] = {0};
snprintf(tmp, 4, "%%%02X", ch);
res += tmp;
}
return res;
}
static char HEXTOI(const char ch)
{
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
return ch - '0';
}
else if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z')
{
return ch - 'a' + 10;
}
else if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')
{
return ch - 'A' + 10;
}
else
return -1;
}
static std::string UrlDecode(const std::string &url, bool convert_plus_to_space)
{
// 遇到了%,则将紧随其后的2个字符,转换为数字,
// 第一个数字左移4位,然后加上第二个数字 + -> 2b %2b->2 << 4 + 11
std::string res;
for (int i = 0; i < url.size(); i++)
{
if (url[i] == '%' && (i + 2) < url.size())
{
char val1 = HEXTOI(url[i + 1]);
char val2 = HEXTOI(url[i + 2]);
char val = val1 * 16 + val2;
i += 2;
res += val;
continue;
}
if (url[i] == '+' && convert_plus_to_space)
{
res += ' ';
continue;
}
res += url[i];
}
return res;
}
// 响应状态码的描述信息获取
static std::string StatuDesc(int statu)
{
auto it = _statu_msg.find(statu);
if (it != _statu_msg.end())
{
return it->second;
}
return "UnKnown";
}
// 根据文件后缀名获取文件mime
static std::string ExtMime(const std::string &filename)
{
// a.b.txt 先获取文件扩展名
size_t pos = filename.rfind(".");
if (pos == std::string::npos)
{
return "application/octet-stream";
}
// 根据扩展名,获取mime
std::string ext = filename.substr(pos);
auto it = _mime_msg.find(ext);
if (it == _mime_msg.end())
{
return "application/octet-stream";
}
return it->second;
}
// 判断一个文件是否是一个目录
static bool IsDirectory(const std::string &filename)
{
struct stat st;
// stat 函数用于获取文件的状态信息,包括文件大小、权限、最后访问时间等
// int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int ret = stat(filename.c_str(), &st);
if (ret < 0)
{
return false;
}
// S_ISDIR 是一个用于检查文件类型的宏,通常在 2.HttpRequest请求类实现
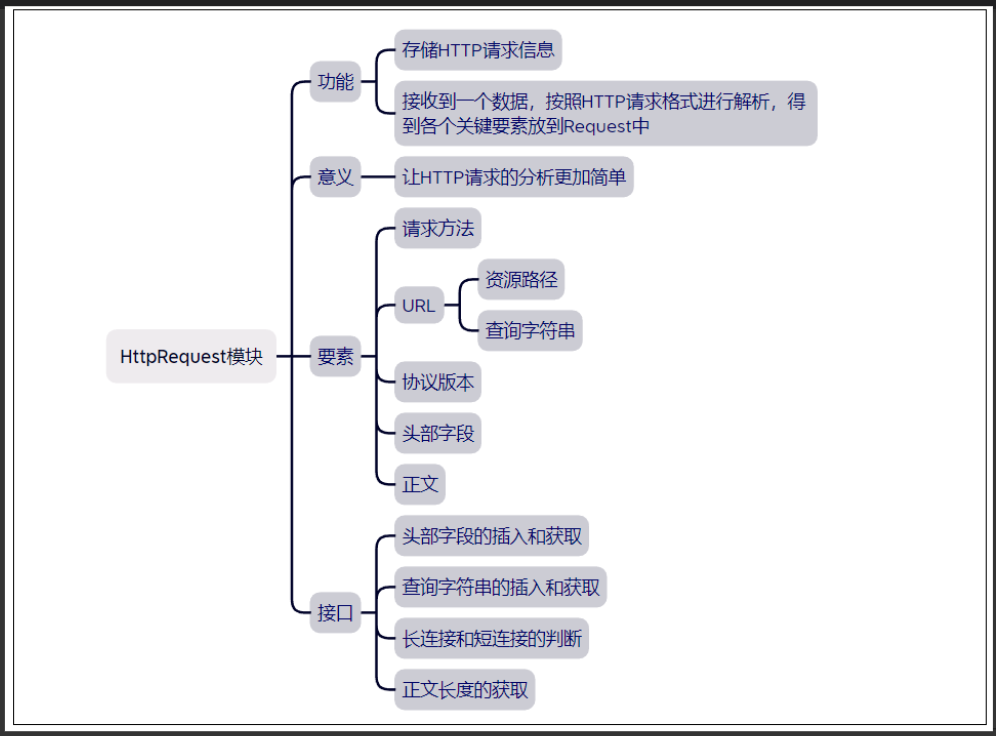
class HttpRequest
{
public:
std::string _method; // 请求方法
std::string _path; // 资源路径
std::string _version; // 协议版本
std::string _body; // 请求正文
std::smatch _matches; // 资源路径的正则提取数据
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers; // 头部字段
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _params; // 查询字符串
public:
HttpRequest() : _version("HTTP/1.1") {}
void ReSet()
{
_method.clear();
_path.clear();
_version = "HTTP/1.1";
_body.clear();
std::smatch match;
_matches.swap(match);
_headers.clear();
_params.clear();
}
// 插入头部字段
void SetHeader(const std::string &key, const std::string &value)
{
_headers.insert(std::make_pair(key, value));
}
// 判断是否存在指定头部字段
bool HasHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end())
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 获取指定头部字段的值
std::string GetHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end())
{
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
// 插入查询字符串
void SetParam(const std::string &key, const std::string &val)
{
_params.insert(std::make_pair(key, val));
}
// 判断是否有某个指定的查询字符串
bool HasParam(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _params.find(key);
if (it == _params.end())
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 获取指定的查询字符串
std::string GetParam(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _params.find(key);
if (it == _params.end())
{
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
size_t ContentLength() const
{
// Content-Length: 1234
bool ret = HasHeader("Content-Length");
if (ret == false)
{
return 0;
}
std::string clen = GetHeader("Content-Length");
return std::stol(clen);
}
// 判断是否是短链接
bool Close() const
{
// 没有Connection字段,或者有Connection但是值是close,则都是短链接,否则就是长连接
if (HasHeader("Connection") && GetHeader("Connection") == "keep-alive")
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
3.HttpResponse响应类实现
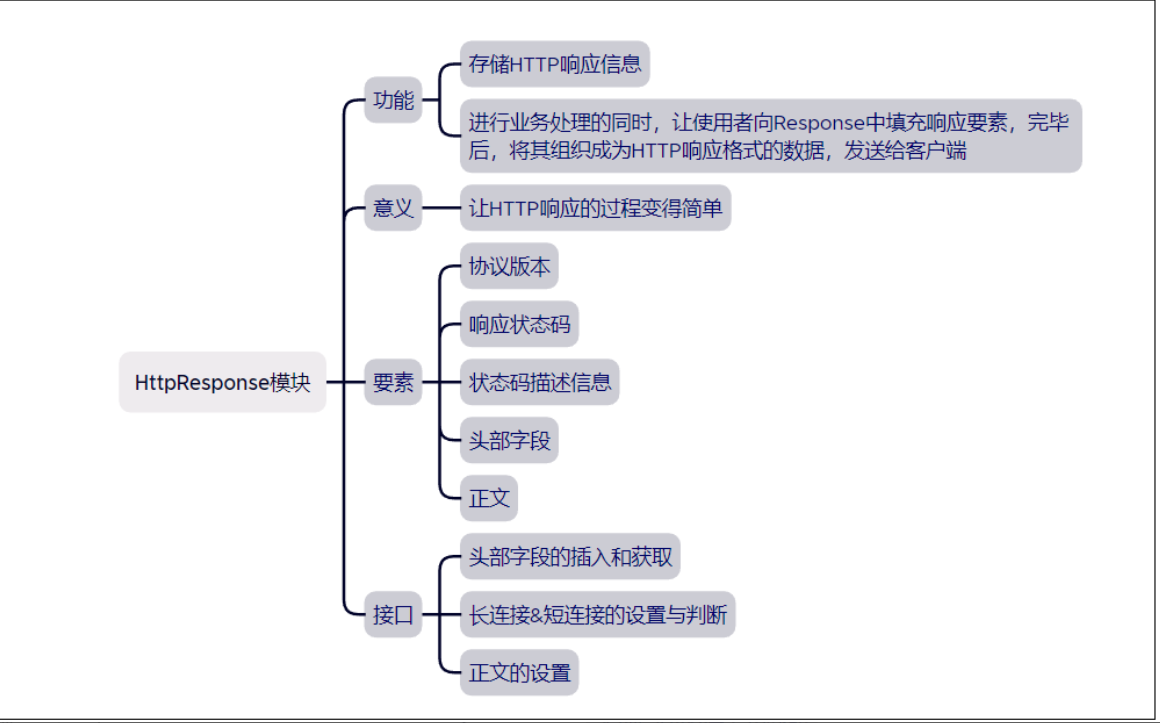
class HttpResponse
{
public:
int _statu; // 响应状态码
bool _redirect_flag; // 是否重定向标志
std::string _body; // 正文
std::string _redirect_url; // 重定向的url
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _headers; // 头部字段
public:
HttpResponse() : _statu(200), _redirect_flag(false) {}
HttpResponse(int statu) : _statu(statu), _redirect_flag(false) {}
void ReSet()
{
_statu = 200;
_redirect_flag = false;
_body.clear();
_redirect_url.clear();
_headers.clear();
}
// 插入头部字段
void SetHeader(const std::string &key, const std::string &value)
{
_headers.insert(std::make_pair(key, value));
}
// 判断是否存在指定头部字段
bool HasHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end())
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 获取指定头部字段的值
std::string GetHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end())
{
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
// 设置正文
void SetContent(const std::string &body, const std::string &type = "text/html")
{
_body = body;
SetHeader("Content-Length", type);
}
// 设置重定向
void SetRedirect(const std::string &url, const int statu = 302)
{
_statu = statu;
_redirect_flag = true;
_redirect_url = url;
}
// 判断是否是短链接
bool Close()
{
// 没有Connection字段,或者有Connection但是值是close,则都是短链接,否则就是长连接
if (HasHeader("Connection") == true && GetHeader("Connection") == "keep-alive")
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
4.HttpContext上下文类实现
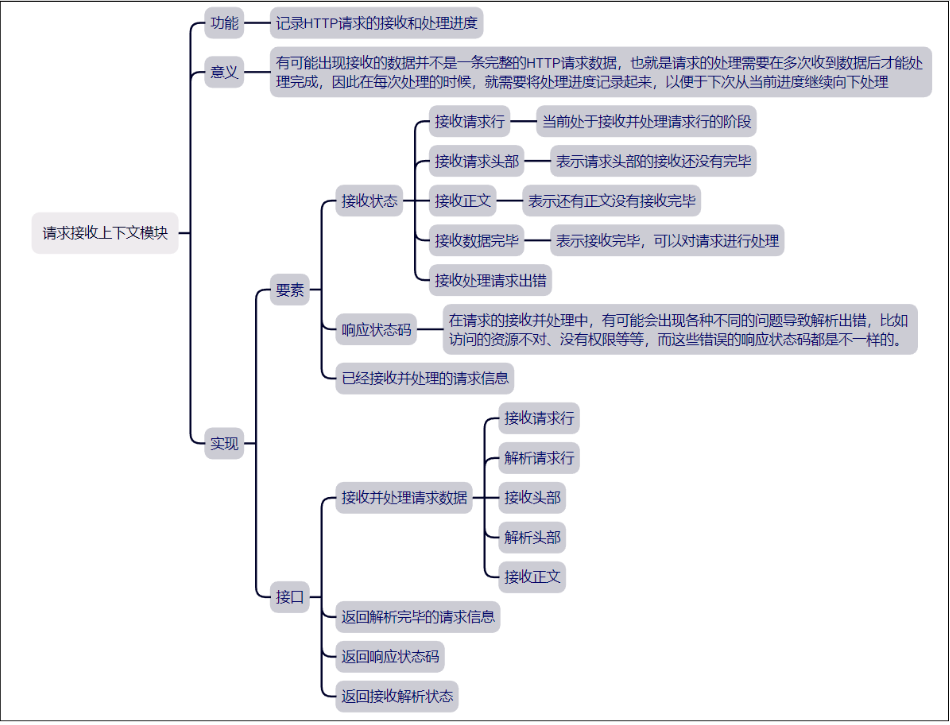
#define MAX_LINE 8192
typedef enum
{
RECV_HTTP_ERROR,
RECV_HTTP_LINE,
RECV_HTTP_HEAD,
RECV_HTTP_BODY,
RECV_HTTP_OVER
} HttpRecvStatu;
class HttpContext
{
private:
int _resp_statu; // 响应状态码
HttpRecvStatu _recv_statu; // 当前接收及解析的阶段状态
HttpRequest _request; // 已经解析得到的请求信息
private:
bool PraseHttpLine(std::string &line)
{
std::smatch matches;
std::regex e("(GET|HEAD|POST|PUT|DELETE) ([^?]*)(?:?(.*))? (HTTP/1.[01])(?:
|
)?", std::regex::icase);
bool ret = std::regex_match(line, matches, e);
if (ret == false)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 400; // BAD REQUEST
return false;
}
// 0 : GET /www.baidu/login?user=xiaoming&pass=123123 HTTP/1.1
// 1 : GET
// 2 : /bitejiuyeke/login
// 3 : user=xiaoming&pass=123123
// 4 : HTTP/1.1
// 请求方法的获取
_request._method = matches[1];
std::transform(_request._method.begin(), _request._method.end(), _request._method.begin(), ::toupper);
// 资源路径的获取,需要进行URL解码操作,但是不需要+转空格
_request._path = Util::UrlDecode(matches[2], false);
// 协议版本的获取
_request._version = matches[4];
// 查询字符串的获取与处理
std::vector<std::string> query_string_array;
std::string query_string = matches[3];
// 查询字符串的格式 key=val&key=val....., 先以 & 符号进行分割,得到各个字串
Util::Split(query_string, "&", &query_string_array);
// 针对各个字串,以 = 符号进行分割,得到key 和val, 得到之后也需要进行URL解码
for (auto &str : query_string_array)
{
size_t pos = str.find("=");
if (pos == std::string::npos)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 400; // BAD REQUEST
return false;
}
std::string key = Util::UrlDecode(str.substr(0, pos), true);
std::string value = Util::UrlDecode(str.substr(pos + 1), true);
_request.SetParam(key, value);
}
return true;
}
bool RecvHttpLine(Buffer *buf)
{
if (_recv_statu != RECV_HTTP_LINE)
return false;
// 1. 获取一行数据,带有末尾的换行
std::string line = buf->GetOneLineAndPop();
// 2. 需要考虑的一些要素:缓冲区中的数据不足一行, 获取的一行数据超大
if (line.size() == 0)
{
// 缓冲区中的数据不足一行,则需要判断缓冲区的可读数据长度,如果很长了都不足一行,这是有问题的
if (buf->ReadAbleSize() > MAX_LINE)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 414; // URI TOO LONG
return false;
}
// 缓冲区中数据不足一行,但是也不多,就等等新数据的到来
return true;
}
if (line.size() > MAX_LINE)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 414; // URI TOO LONG
return false;
}
bool ret = PraseHttpLine(line);
if (ret == false)
{
return false;
}
// 首行处理完毕,进入头部获取阶段
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_HEAD;
return true;
}
bool RecvHttpHead(Buffer *buf)
{
if (_recv_statu != RECV_HTTP_HEAD)
return false;
// 一行一行取出数据,直到遇到空行为止, 头部的格式 key: val
key: val
....
while (true)
{
std::string line = buf->GetOneLineAndPop();
if (line.size() == 0)
{
// 缓冲区中的数据不足一行,则需要判断缓冲区的可读数据长度,如果很长了都不足一行,这是有问题的
if (buf->ReadAbleSize() > MAX_LINE)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 414; // URI TOO LONG
return false;
}
// 缓冲区中数据不足一行,但是也不多,就等等新数据的到来
return true;
}
if (line.size() > MAX_LINE)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 414; // URI TOO LONG
return false;
}
if (line == "
" || line == "
")
{
break;
}
bool ret = PraseHttpHead(line);
if (ret == false)
return false;
}
// 头部处理完毕,进入正文获取阶段
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_BODY;
return true;
}
bool PraseHttpHead(std::string &line)
{
// key: val
key: val
....
if (line.back() == '
')
line.pop_back(); // 末尾是换行则去掉换行字符
if (line.back() == '
')
line.pop_back(); // 末尾是回车则去掉回车字符
size_t pos = line.find(": ");
if (pos == std::string::npos)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 400; // BAD REQUEST
return false;
}
std::string key = line.substr(0, pos);
std::string value = line.substr(pos + 2);
_request.SetHeader(key, value);
return true;
}
bool RecvHttpBody(Buffer *buf)
{
if (_recv_statu != RECV_HTTP_BODY)
return false;
// 1. 获取正文长度
size_t content_length = _request.ContentLength();
if (content_length == 0)
{
// 没有正文,则请求接收解析完毕
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_OVER;
return true;
}
// 2. 当前已经接收了多少正文,其实就是往 _request._body 中放了多少数据了
size_t real_length = content_length - _request._body.size();
// 3. 接收正文放到body中,但是也要考虑当前缓冲区中的数据,是否是全部的正文
// 3.1 缓冲区中数据,包含了当前请求的所有正文,则取出所需的数据
if (real_length <= buf->ReadAbleSize())
{
_request._body.append(buf->ReadPosition(), real_length);
buf->MoveReadOffset(real_length);
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_OVER;
return true;
}
// 3.2 缓冲区中数据,无法满足当前正文的需要,数据不足,取出数据,然后等待新数据到来
_request._body.append(buf->ReadPosition(), buf->ReadAbleSize());
buf->MoveReadOffset(buf->ReadAbleSize());
return true;
}
public:
HttpContext() : _resp_statu(200), _recv_statu(RECV_HTTP_LINE) {}
void ReSet()
{
_resp_statu = 200;
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_LINE;
_request.ReSet();
}
int RespStatu() { return _resp_statu; }
HttpRecvStatu RecvStatu() { return _recv_statu; }
HttpRequest &Request() { return _request; }
// 接收并解析HTTP请求
void RecvHttpRequest(Buffer *buf)
{
// 不同的状态,做不同的事情,但是这里不要break
// 因为处理完请求行后,应该立即处理头部,而不是退出等新数据
switch (_recv_statu)
{
case RECV_HTTP_LINE:
RecvHttpLine(buf);
case RECV_HTTP_HEAD:
RecvHttpHead(buf);
case RECV_HTTP_BODY:
RecvHttpBody(buf);
}
}
};
5.HttpServer类实现
#define DEFAULT_TIME_OUT 30
class HttpServer
{
private:
using Handler = std::function<void(const HttpRequest &, HttpResponse *)>;
using Handlers = std::vector<std::pair<std::regex, Handler>>;
Handlers _get_route;
Handlers _post_route;
Handlers _put_route;
Handlers _delete_route;
std::string _basedir; // 静态资源根目录
TcpServer _server;
private:
void ErrorHandler(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
// 1. 组织一个错误展示页面
std::string body;
body += "";
body += "";
body += "";
body += "";
body += "";
body += ""
;
body += std::to_string(rsp->_statu);
body += " ";
body += Util::StatuDesc(rsp->_statu);
body += "";
body += "";
body += "";
// 2. 将页面数据,当作响应正文,放入rsp中
rsp->SetContent(body, "text/html");
}
// 将HttpResponse中的要素按照http协议格式进行组织发送
void WriteResponse(const PtrConnection &conn, const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &rsp)
{
// 1. 先完善头部字段
if (req.Close() == true)
rsp.SetHeader("Connection", "close");
else
rsp.SetHeader("Connection", "keep-alive");
if (rsp._body.empty() == false && rsp.HasHeader("Content-Length") == false)
{
rsp.SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(rsp._body.size()));
}
if (rsp._body.empty() == false && rsp.HasHeader("Content-Type") == false)
{
rsp.SetHeader("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream");
}
if (rsp._redirect_flag == true)
{
rsp.SetHeader("Location", rsp._redirect_url);
}
// 2. 将rsp中的要素,按照http协议格式进行组织
std::stringstream rsp_str;
rsp_str << req._version << " " << std::to_string(rsp._statu) << " "
<< Util::StatuDesc(rsp._statu) << "
";
// for (auto &head : rsp._headers)
// {
// rsp_str << head.first << ": " << head.second << "
";
// }
for (auto &[key, val] : rsp._headers)
{
rsp_str << key << ": " << val << "
";
}
rsp_str << "
";
rsp_str << rsp._body;
// 3. 发送数据
conn->Send(rsp_str.str().c_str(), rsp_str.str().size());
}
// 功能性请求的分类处理
void Dispatcher(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp, Handlers &handlers)
{
// 在对应请求方法的路由表中,查找是否含有对应资源请求的处理函数,有则调用,没有则返回404
// 思想:路由表存储的时键值对 -- 正则表达式 & 处理函数
// 使用正则表达式,对请求的资源路径进行正则匹配,匹配成功就使用对应函数进行处理
// /numbers/(d+) /numbers/12345
for (auto &handler : handlers)
{
const std::regex &re = handler.first;
const Handler &functor = handler.second;
bool ret = std::regex_match(req._path, req._matches, re);
if (ret == false)
continue;
// 传入请求信息,和空的rsp,执行处理函数
return functor(req, rsp);
}
rsp->_statu = 404;
}
// 判断是否为静态资源请求
bool IsFileHandler(const HttpRequest &req)
{
// 1. 必须设置了静态资源根目录
if (_basedir.empty())
return false;
// 2. 请求方法,必须是GET / HEAD请求方法
if (req._method != "GET" && req._method != "HEAD")
return false;
// 3. 请求的资源路径必须是一个合法路径
if (Util::ValidPath(req._path) == false)
return false;
// 4. 请求的资源必须存在,且是一个普通文件
// 有一种请求比较特殊 -- 目录:/, /image/, 这种情况给后边默认追加一个 index.html
// index.html /image/a.png
// 不要忘了前缀的相对根目录,也就是将请求路径转换为实际存在的路径
// /image/a.png -> ./wwwroot/image/a.png
std::string req_path = _basedir + req._path;
if (req_path.back() == '/')
{
req_path += "index.html";
}
if (Util::IsRegular(req_path) == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// 静态资源请求的处理
void FileHandler(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
std::string req_path = _basedir + req._path;
if (req_path.back() == '/')
req_path += "index.html";
bool ret = Util::ReadFile(req_path, &rsp->_body);
if (ret == false)
return;
std::string mime = Util::ExtMime(req_path);
rsp->SetHeader("Content-Type", mime);
return;
}
void Route(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
// 1. 对请求进行分辨,是一个静态资源请求,还是一个功能性请求
// 静态资源请求,则进行静态资源的处理
// 功能性请求,则需要通过几个请求路由表来确定是否有处理函数
// 既不是静态资源请求,也没有设置对应的功能性请求处理函数,就返回405
if (IsFileHandler(req) == true)
{
// 是一个静态资源请求, 则进行静态资源请求的处理
return FileHandler(req, rsp);
}
if (req._method == "GET" || req._method == "HEAD")
return Dispatcher(req, rsp, _get_route);
else if (req._method == "POST")
return Dispatcher(req, rsp, _post_route);
else if (req._method == "PUT")
return Dispatcher(req, rsp, _put_route);
else if (req._method == "DELETE")
return Dispatcher(req, rsp, _delete_route);
rsp->_statu = 405; // Method Not Allowed
return;
}
// 设置上下文
void OnConnected(const PtrConnection &conn)
{
conn->SetContext(HttpContext());
LogMessage(NORMAL, "NEW CONNECTION %p", conn.get());
}
// 缓冲区数据解析+处理
void OnMessage(const PtrConnection &conn, Buffer *buf)
{
while (buf->ReadAbleSize() > 0)
{
// 1. 获取上下文
HttpContext *context = conn->GetContext()->get<HttpContext>();
// 2. 通过上下文对缓冲区数据进行解析,得到HttpRequest对象
// 1. 如果缓冲区的数据解析出错,就直接回复出错响应
// 2. 如果解析正常,且请求已经获取完毕,才开始去进行处理
context->RecvHttpRequest(buf);
HttpRequest &req = context->Request();
HttpResponse rsp(context->RespStatu());
if (context->RespStatu() >= 400)
{
// 进行错误响应,关闭连接
// 填充一个错误显示页面数据到rsp中
ErrorHandler(req, &rsp);
// 组织响应发送给客户端
WriteResponse(conn, req, rsp);
context->ReSet();
// 出错了就把缓冲区数据清空
buf->MoveReadOffset(buf->ReadAbleSize());
// 关闭连接
conn->Shutdown();
return;
}
// 当前请求还没有接收完整,则退出,等新数据到来再重新继续处理
if (context->RecvStatu() != RECV_HTTP_OVER)
return;
// 3. 请求路由 + 业务处理
Route(req, &rsp);
// 4. 对HttpResponse进行组织发送
WriteResponse(conn, req, rsp);
// 5. 重置上下文
context->ReSet();
// 6. 根据长短连接判断是否关闭连接或者继续处理--//短链接则直接关闭
if (rsp.Close() == true)
{
conn->Shutdown();
}
}
}
public:
HttpServer(int port, int timeout = DEFAULT_TIME_OUT) : _server(port)
{
_server.EnableInactiveRelease(timeout);
_server.SetConnectedCallback(std::bind(&HttpServer::OnConnected, this, std::placeholders::_1));
_server.SetMessageCallback(std::bind(&HttpServer::OnMessage, this,
std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2));
}
// 设置资源根目录
void SetBaseDir(const std::string &path) { _basedir = path; }
// 设置各种请求方法的回调函数
void Get(const std::string &pattern, const Handler &handler)
{
_get_route.push_back(std::make_pair(std::regex(pattern), handler));
}
void Post(const std::string &pattern, const Handler &handler)
{
_post_route.push_back(std::make_pair(std::regex(pattern), handler));
}
void Put(const std::string &pattern, const Handler &handler)
{
_put_route.push_back(std::make_pair(std::regex(pattern), handler));
}
void Delete(const std::string &pattern, const Handler &handler)
{
_delete_route.push_back(std::make_pair(std::regex(pattern), handler));
}
// 设置线程数量
void SetThreadCount(int count) { _server.SetThreadCount(count); }
// 启动服务器
void Listen() { _server.Start(); }
};
6.HttpServer 简单测试
#include "./http.hpp"
#define WWWROOT "./wwwroot/"
std::string RequestStr(const HttpRequest &req)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << req._method << " " << req._path << " " << req._version << "
";
for (auto &[key, val] : req._params)
{
ss << key << ": " << val << "
";
}
for (auto &[key, val] : req._headers)
{
ss << key << ": " << val << "
";
}
ss << "
";
ss << req._body;
return ss.str();
}
void Hello(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
rsp->SetContent(RequestStr(req), "text/plain");
}
void Login(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
rsp->SetContent(RequestStr(req), "text/plain");
}
void PutFile(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
std::string pathname = WWWROOT + req._path;
Util::WriteFile(pathname, req._body);
}
void DelFile(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
rsp->SetContent(RequestStr(req), "text/plain");
}
int main()
{
HttpServer server(8080);
server.SetThreadCount(3);
server.SetBaseDir(WWWROOT);
server.Get("/hello", Hello);
server.Post("/login", Login);
server.Put("/1234.txt", PutFile);
server.Delete("/1234.txt", DelFile);
server.Listen();
return 0;
}
|-- echo
| |-- echo.hpp
| |-- main.cc
| `-- makefile
|-- http
| |-- http.hpp // HttpServer
| |-- main
| |-- main.cc // 测试程序
| |-- makefile
| `-- wwwroot //静态资源根目录
| |-- 1234.txt
| `-- index.html
|-- log.hpp
|-- main.cc
|-- makefile
`-- server.hpp // TcpServer
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf8">
head>
<body>
<form action="/login" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username"><br/>
<input type="password" name="password"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" name="submit">
form>
body>
html>
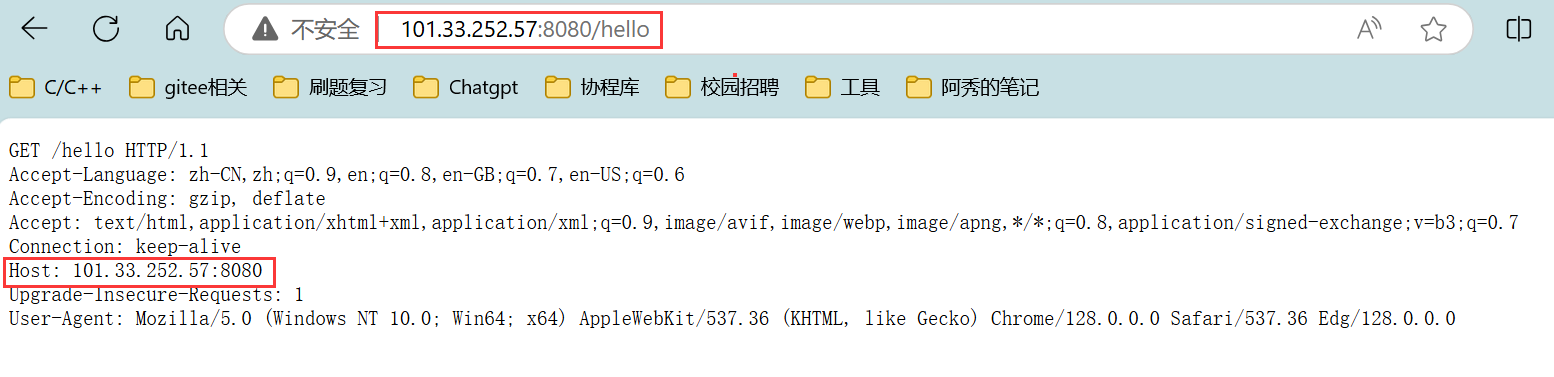
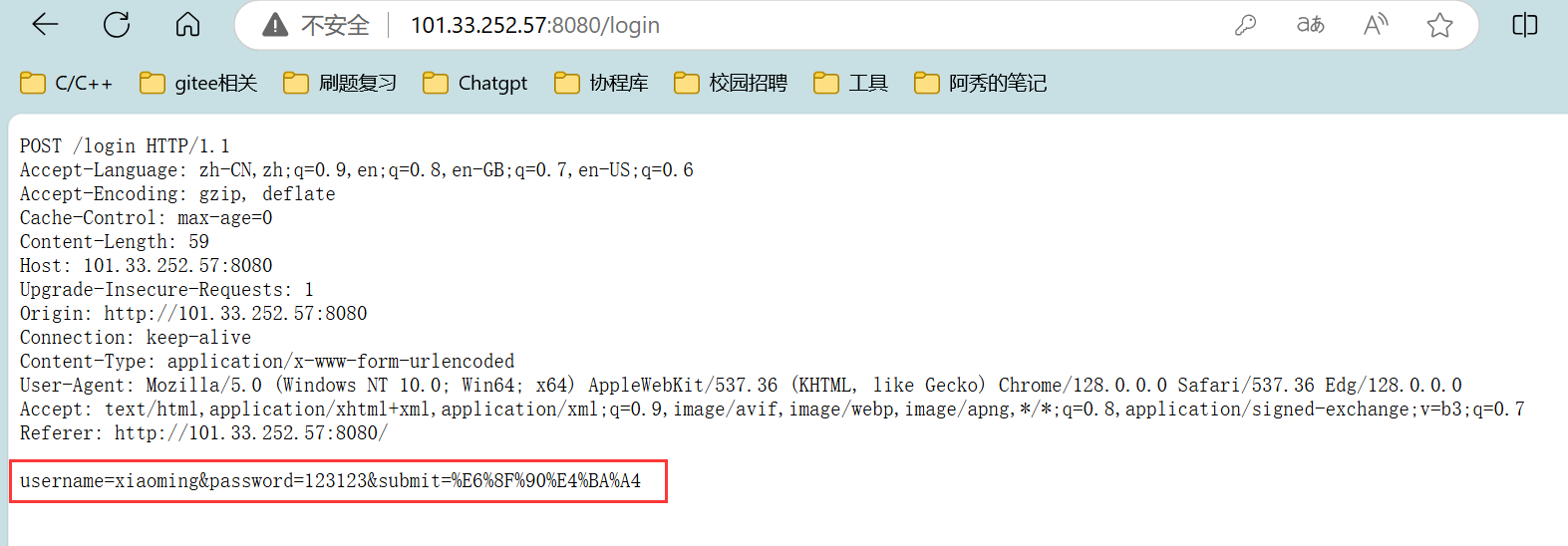
八、性能测试
1. 服务器长连接测试
/**
* @details 长连接测试1:创建一个客户端持续给服务器发送数据,直到超过超时时间看看是否正常
*/
#include "../source/server.hpp"
int main()
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
for (;;)
{
int ret = clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size());
assert(ret > 0);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
ret = clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023);
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
sleep(3);
}
clientsock.Close();
return 0;
}

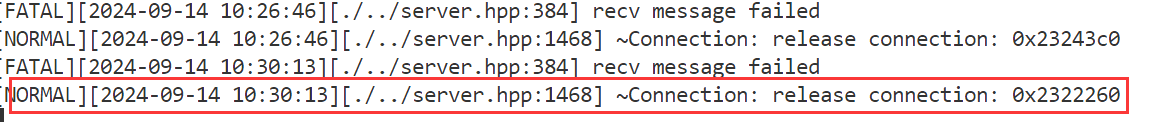
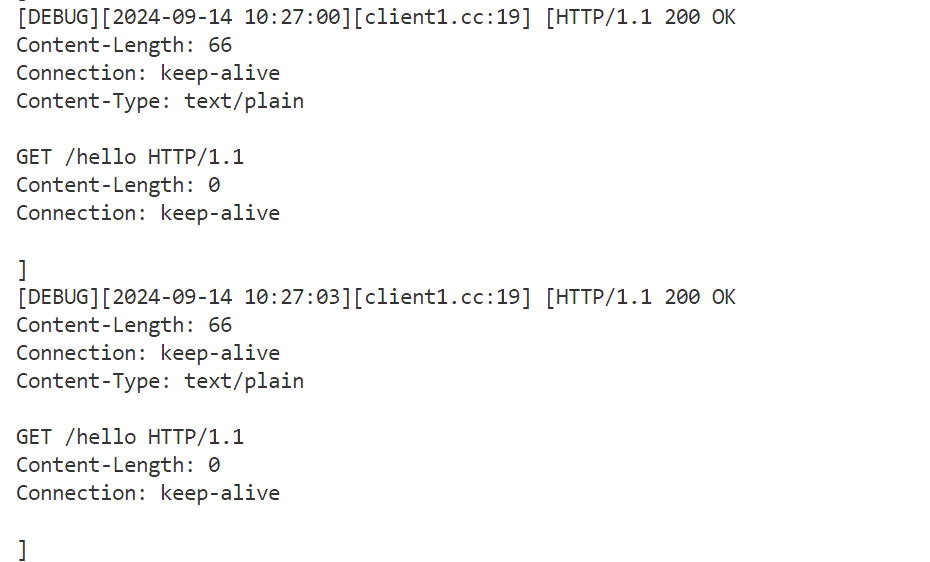
2. 服务器超时连接测试
/**
* @brief 超时连接测试1:创建一个客户端,给服务器发送一次数据之后,不动了,查看服务器是否会正常的超时关闭连接
*/
#include "../source/server.hpp"
int main()
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
for (;;)
{
int ret = clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size());
assert(ret > 0);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
ret = clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023);
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
sleep(15);
}
clientsock.Close();
return 0;
}
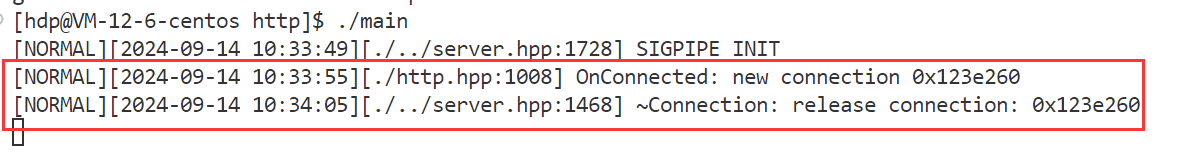
3.服务器错误请求测试
/**
* @brief 给服务器发送一个数据,告诉服务器要发送1024字节的数据,但是实际发送的数据不足1024,查看服务器处理结果
* @details 1.如果服务器只发送一次,服务器将得不到完整的请求,就不会处理业务,客户端也就得不到响应,最终超时关闭连接
* 2.连着给服务器发送了多次 小的请求,服务器会将后边的请求当做前边请求的正文来进行处理,
* 而后便处理的时候有可能就因为处理错误而关闭连接
*/
/**
* @details 连着给服务器发送了多次 小的请求,服务器解析出错,返回错误,关闭连接,
* 但是关闭连接的时候如果缓冲区里面有数据,由不足一行数据,取不出来,而关闭连接的时候有数据又会启动
* 有消息的事件,就会再次触发OnMassage回调函数,一直循环,解决办法,解析出错,就情况缓冲区的数据
* 第一次解析错误的时候,状态码为RECV_HTTP_ERROR,没有更新状态,那么下次再进去的时候,状态还是RECV_HTTP_ERROR
* 此时解析http的函数并不会读取数据,所以缓冲区中的数据一直处理不完,解决办法重置状态
*/
#include "../source/server.hpp"
int main()
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 100
Hello world";
for (;;)
{
assert(clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
assert(clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
assert(clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
assert(clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
assert(clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023));
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
sleep(3);
}
clientsock.Close();
return 0;
}
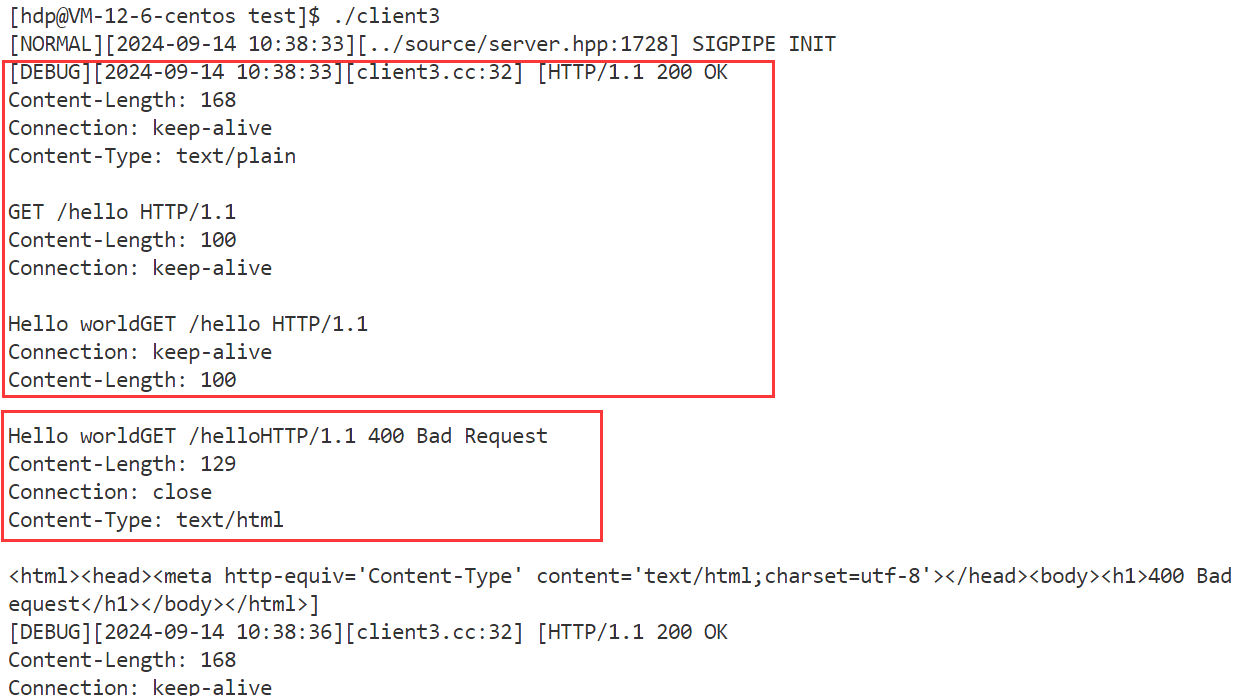
4.服务器业务处理超时测试
/* 业务处理超时,查看服务器的处理情况
当服务器达到了一个性能瓶颈,在一次业务处理中花费了太长的时间(超过了服务器设置的非活跃超时时间)
1. 在一次业务处理中耗费太长时间,导致其他的连接也被连累超时,其他的连接有可能会被拖累超时释放
假设现在 12345描述符就绪了, 在处理1的时候花费了30s处理完,超时了,导致2345描述符因为长时间没有刷新活跃度
1. 如果接下来的2345描述符都是通信连接描述符,如果都就绪了,则并不影响,因为接下来就会进行处理并刷新活跃度
2. 如果接下来的2号描述符是定时器事件描述符,定时器触发超时,执行定时任务,就会将345描述符给释放掉
这时候一旦345描述符对应的连接被释放,接下来在处理345事件的时候就会导致程序崩溃(内存访问错误)
因此这时候,在本次事件处理中,并不能直接对连接进行释放,而应该将释放操作压入到任务池中,
等到事件处理完了执行任务池中的任务的时候,再去释放
*/
/**
* 对于释放连接,ShutDownInLoop 不应该立即进行释放ReleaseInLoop,而是应该压入任务队列中
* 这样就不需要在只要有读写事件之前就刷新一次活跃度,只需要在业务处理完毕之后刷新活跃度即可
* OnTime() 定时器需要返回当前超时的次数,来进行执行超时任务
* // 根据实际超时的次数,执行对应的超时任务
*/
#include "../source/server.hpp"
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
LogMessage(ERROR, "fork error");
return -1;
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
for (;;)
{
int ret = clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size());
assert(ret > 0);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
ret = clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023);
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
}
clientsock.Close();
exit(0);
}
}
while(1) sleep(1);
return 0;
}
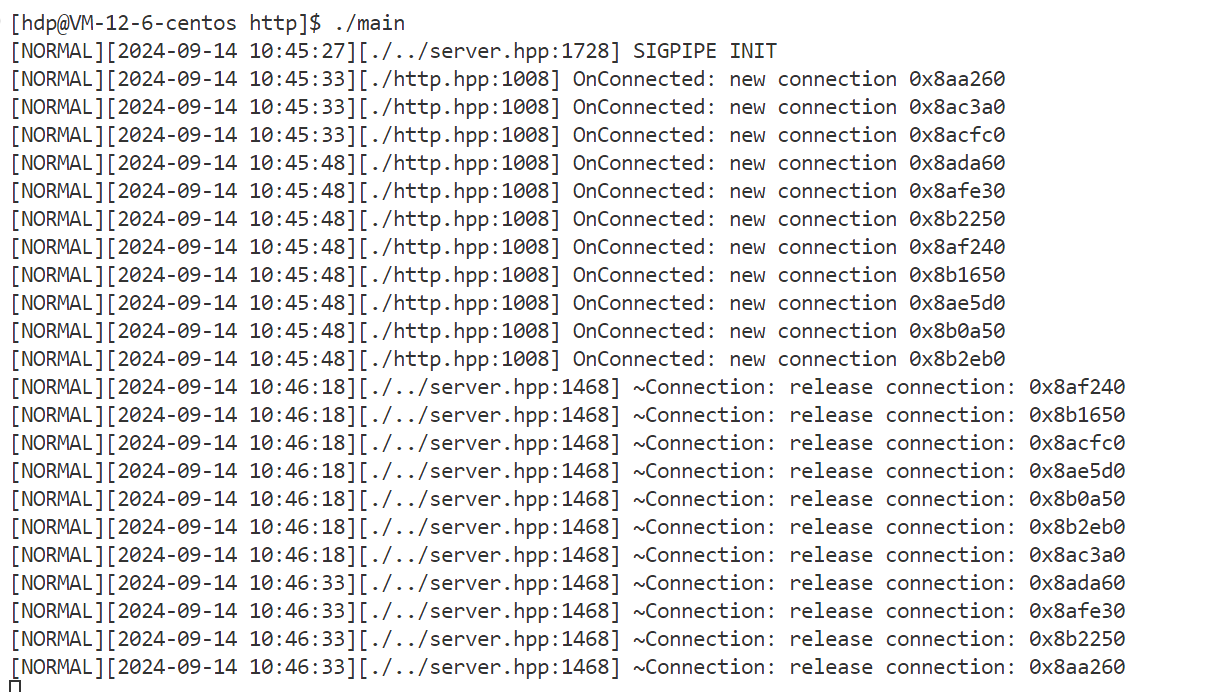
5.服务器同时多条请求测试
/*一次性给服务器发送多条数据,然后查看服务器的处理结果*/
/*每一条请求都应该得到正常处理*/
#include "../source/server.hpp"
int main()
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
req += "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
req += "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
for (;;)
{
int ret = clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size());
assert(ret > 0);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
ret = clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023);
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
sleep(3);
}
clientsock.Close();
return 0;
}

服务器大文件传输测试
/**
* 大文件传输测试,给服务器上传一个大文件,服务器将文件保存下来,观察处理结果
* 上次的文件和服务器保存的文件一致
*/
// 创建一个大文件
// dd if=/dev/zero of=./hello.txt bs=1G count=1
#include "../source/server.hpp"
#include "../source/http/http.hpp"
int main()
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "PUT /1234.txt HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
";
std::string body;
Util::ReadFile("./hello.txt", &body);
req += "Content-Length: " + std::to_string(body.size()) + "
";
assert(clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
assert(clientsock.Send(body.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
assert(clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023) != -1);
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
sleep(15);
clientsock.Close();
return 0;
}
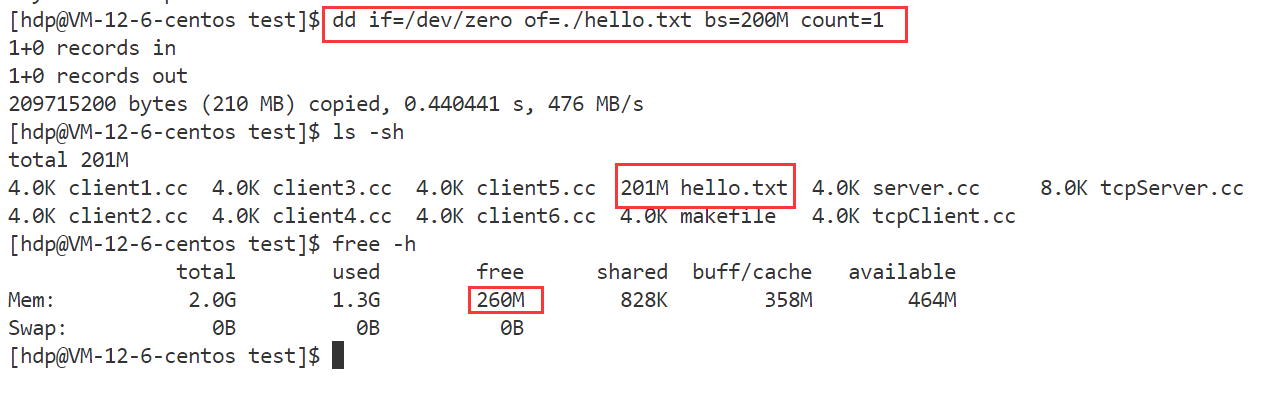

服务器性能压力测试
./webbench -c 1000 -t 3600 http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello

4.服务器业务处理超时测试
/* 业务处理超时,查看服务器的处理情况
当服务器达到了一个性能瓶颈,在一次业务处理中花费了太长的时间(超过了服务器设置的非活跃超时时间)
1. 在一次业务处理中耗费太长时间,导致其他的连接也被连累超时,其他的连接有可能会被拖累超时释放
假设现在 12345描述符就绪了, 在处理1的时候花费了30s处理完,超时了,导致2345描述符因为长时间没有刷新活跃度
1. 如果接下来的2345描述符都是通信连接描述符,如果都就绪了,则并不影响,因为接下来就会进行处理并刷新活跃度
2. 如果接下来的2号描述符是定时器事件描述符,定时器触发超时,执行定时任务,就会将345描述符给释放掉
这时候一旦345描述符对应的连接被释放,接下来在处理345事件的时候就会导致程序崩溃(内存访问错误)
因此这时候,在本次事件处理中,并不能直接对连接进行释放,而应该将释放操作压入到任务池中,
等到事件处理完了执行任务池中的任务的时候,再去释放
*/
/**
* 对于释放连接,ShutDownInLoop 不应该立即进行释放ReleaseInLoop,而是应该压入任务队列中
* 这样就不需要在只要有读写事件之前就刷新一次活跃度,只需要在业务处理完毕之后刷新活跃度即可
* OnTime() 定时器需要返回当前超时的次数,来进行执行超时任务
* // 根据实际超时的次数,执行对应的超时任务
*/
#include "../source/server.hpp"
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
LogMessage(ERROR, "fork error");
return -1;
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
for (;;)
{
int ret = clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size());
assert(ret > 0);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
ret = clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023);
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
}
clientsock.Close();
exit(0);
}
}
while(1) sleep(1);
return 0;
}

5.服务器同时多条请求测试
/*一次性给服务器发送多条数据,然后查看服务器的处理结果*/
/*每一条请求都应该得到正常处理*/
#include "../source/server.hpp"
int main()
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
req += "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
req += "GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 0
";
for (;;)
{
int ret = clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size());
assert(ret > 0);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
ret = clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023);
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
sleep(3);
}
clientsock.Close();
return 0;
}

服务器大文件传输测试
/**
* 大文件传输测试,给服务器上传一个大文件,服务器将文件保存下来,观察处理结果
* 上次的文件和服务器保存的文件一致
*/
// 创建一个大文件
// dd if=/dev/zero of=./hello.txt bs=1G count=1
#include "../source/server.hpp"
#include "../source/http/http.hpp"
int main()
{
// 创建客户端连接
Socket clientsock;
clientsock.CreateClient(8080, "127.0.0.1");
std::string req = "PUT /1234.txt HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
";
std::string body;
Util::ReadFile("./hello.txt", &body);
req += "Content-Length: " + std::to_string(body.size()) + "
";
assert(clientsock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
assert(clientsock.Send(body.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
char buffer[1024] = {0};
assert(clientsock.Recv(buffer, 1023) != -1);
LogMessage(DEBUG, "[%s]", buffer);
sleep(15);
clientsock.Close();
return 0;
}



服务器性能压力测试
./webbench -c 1000 -t 3600 http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello